imported>Makaos |
imported>Andy |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{TOCright}}
| + | = Defining Translations Using The Theory Plug-in = |
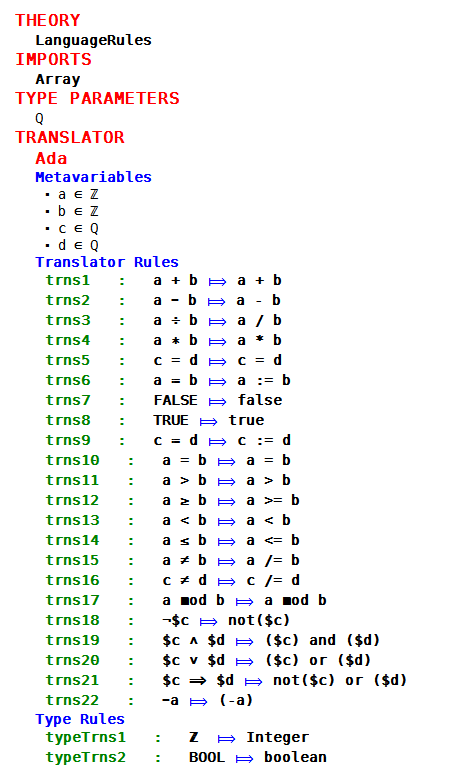
| | + | The theory plug-in is used to add mathematical extensions to Rodin. The theories are created, and deployed, and can then be used in any models in the workspace. When dealing with implementation level models, such as in Tasking Event-B, we need to consider how to translate newly added types and operators into code. We have augmented the theory interface with a Translation Rules section. This enables a user to define translation rules that map Event-B formulas to code. |
| | + | == Translation Rules== |
| | + | <div id="fig:Translation Rules"> |
| | + | <br/> |
| | + | [[Image:TheoryCGRules.png|center||caption text]] |
| | + | <center>'''Figure 1''': Translation Rules</center> |
| | + | <br/> |
| | + | </div> |
| | | | |
| | + | Figure 1 shows the interface, and some translations rules of the mapping to Ada. |
| | | | |
| − | = Rodin User and Developer Workshop July 15-17 2009 =
| + | The theory is given a name, and may import some other theories. Type parameters can be added, and we use them here to type the meta-variables. The meta-variable ''a'' is restricted to be an integer type, but meta-variable ''c'' can be any type. |
| | | | |
| | + | The translator rules are templates used for pattern matching. The meta-variables are defined and typed, and used in the rules. Event-B expressions and predicates are defined on the left hand side of the rule, and the code to be output (as text) appears on the right hand side of the matching rule. |
| | | | |
| − | While much of the continued development and use of Rodin takes place within the DEPLOY Project, there is a growing group of users and plug-in developers outside of DEPLOY. In July 2009, DEPLOY organised a workshop at the University of Southampton to bring together existing and potential users and developers of the Rodin toolset and to foster a broader community of Rodin users and developers. For Rodin users the workshop provided an opportunity to share tool experiences and to gain an understanding of on-going tool developments. For plug-in developers the workshop provided an opportunity to showcase their tools and to achieve better coordination of tool development effort. Moving towards an open source development project will mean that features that cannot be resourced from within the project can be developed outside the project. It will also help to guarantee the longer-term future of the Rodin platform.[http://forexrobot.eu.com/ Forex Robot Eu]
| + | == Type Rules == |
| − | This report contains the abstracts of the presentations at the workshop on 16 and 17 July 2009. The workshop was preceded by a tutorial for Rodin Plug-in developers on 15 July.[http://nic.uoregon.edu/nic-wiki/ForexRobots Forex Robots]
| |
| | | | |
| − | We would like to acknowledge the support of the School of Electronics and Computer Science at the University of Southampton (especially the organisational work of Maggie Bond), the DEPLOY project and additional government funding of site's [http://www.bestessays.com.au term papers], [http://primarytermpapers.com/custom-writing-company custom writing company].
| + | The type rules section, shown in Figure 1, is where the relationship is defined, between Event-B types and the type system of the implementation. |
| | | | |
| − | | + | = Adding new Types = |
| − | '''Organisers'''
| + | In the following example we wish to add a new type to Event-B, and then define its translation to code. |
| − | | |
| − | Michael Butler, University of Southampton
| |
| − | | |
| − | Stefan Hallerstede, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf
| |
| − | | |
| − | Laurent Voisin, Systerel
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | == [http://deploy-eprints.ecs.soton.ac.uk/137/ Report containing the abstracts is available here] ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Slides from presentations ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Wednesday 15 July ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | Laurent Voisin and
| |
| − | Stefan Hallerstede,
| |
| − | [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Rodin_plug-in_tutorial_2009-07-15.pdf Rodin Plug-in Development Tutorial]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Thursday 16 July===
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Michael Butler, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Intro.pdf Introduction]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Ken Robinson, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Rodin-workshop-article.pdf System Modelling and Design: Refining Software Engineering]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Jean-Raymond Abrial, [http://deploy-eprints.ecs.soton.ac.uk/138/ Doing Mathematics with the Rodin Platform]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Stephen Wright, [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/Image:Steve_Wright_Quite_Big_Model_Presentation.pdf Experiences with a Quite Big Event-B Model]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * John Colley, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/ColleyJuly09.pdf On Proving with Event-B that a Pipelined Processor Model Implements its ISA Specification]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Fangfang Yuan, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/soton-workshop.pdf Quantitative Design Decisions Measurement using Formal Method]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Kriangsak Damchoom and Michael Butler, [http://www.event-b.org/rodin09/FlashFileSysRodinWorkshopJuly2009.ppt An Experiment in Applying Event-B and Rodin to a Flash-Based Filestore]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Philipp Ruemmer, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Talk_rodin09_philipp_ruemmer.pdf A Theory of Finite Sets, Lists, and Maps for the SMT-Lib Standard]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Matthias Schmalz, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Atp_improvements.pdf Better automated theorem proving in Event-B]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Issam Maamria, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Proposal_for_Rule-based_prover.pdf Proposal for an extensible rule-based prover for Event-B]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Gudmund Grov, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Reasoned_modelling.pdf A Proposal for a Rodin Proof Planner & Reasoned Modelling Plug-in]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Jens Bendisposto, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Using_and_extending_prob.pdf Using and Extending ProB]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Ilya Lopatkin, Towards the SAL plugin for the Rodin platform
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Kenneth Lausdahl and Miguel Ferreira, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/An_Overview_of_Overture.pdf An Overview of Overture]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Michael Butler, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Roadmap.pdf Roadmap for the Rodin Tool]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Friday 17 July===
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Aryldo G Russo Jr., [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/ICFEM_2009_revised_presentation.pdf Formal Methods Outside the Mother Land ]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Maria Teresa Llano, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/RodinWorkshopPresentation.pdf Systems Evolution via Animation and Reasoning]
| |
| − | * Atif Mashkoor, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/BRANIMATION20090717.pdf BRANIMATION]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Fredrik Degerlund and Richard Grönblom, A Framework for Code Generation and Scheduling of Event-B Models
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Andy Edmunds, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/RodinWorkshop2009.pdf Code Generation from Event-B - Using an Intermediate Specification Notation]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Alexei Iliasov, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Soton_flow.pdf On Event-B and Control Flow]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Michael Jastram, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Requirements-quo-vadis.pdf Requirements Traceability]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Joris Rehm, LORIA, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Timed_machine_plugin_visual.pdf A Rodin plugin for quantitative timed models]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Renato Silva, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Composition,_Renaming_and_Generic_Instantiation.pdf Composition, Renaming and Generic Instantiation in Event-B Development]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Abderrahman Matoussi, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Slides_matoussi_-Southampton-.pdf Expressing KAOS Goal Refinement Patterns with Event-B ]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Eduardo Mazza, A tool for specifying and validating software responsibility
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Mar Yah Said, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Rodin_Workshop_16_July_2009_2.pdf Language and Tool Support for Class and State Machine Refinement in UML-B]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Colin Snook, [http://wiki.event-b.org/images/An_EMF_framework_for_EventB.pdf An EMF Framework for Event-B]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * James Sharp, Using CSP Refusal Specifications to Ensure Event-B Refinement
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | [[Category:Meetings]]
| |
Defining Translations Using The Theory Plug-in
The theory plug-in is used to add mathematical extensions to Rodin. The theories are created, and deployed, and can then be used in any models in the workspace. When dealing with implementation level models, such as in Tasking Event-B, we need to consider how to translate newly added types and operators into code. We have augmented the theory interface with a Translation Rules section. This enables a user to define translation rules that map Event-B formulas to code.
Translation Rules
Figure 1: Translation Rules
Figure 1 shows the interface, and some translations rules of the mapping to Ada.
The theory is given a name, and may import some other theories. Type parameters can be added, and we use them here to type the meta-variables. The meta-variable a is restricted to be an integer type, but meta-variable c can be any type.
The translator rules are templates used for pattern matching. The meta-variables are defined and typed, and used in the rules. Event-B expressions and predicates are defined on the left hand side of the rule, and the code to be output (as text) appears on the right hand side of the matching rule.
Type Rules
The type rules section, shown in Figure 1, is where the relationship is defined, between Event-B types and the type system of the implementation.
Adding new Types
In the following example we wish to add a new type to Event-B, and then define its translation to code.