imported>Son |
imported>Andy |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | == Introduction == | + | == The Theory Plug-in == |
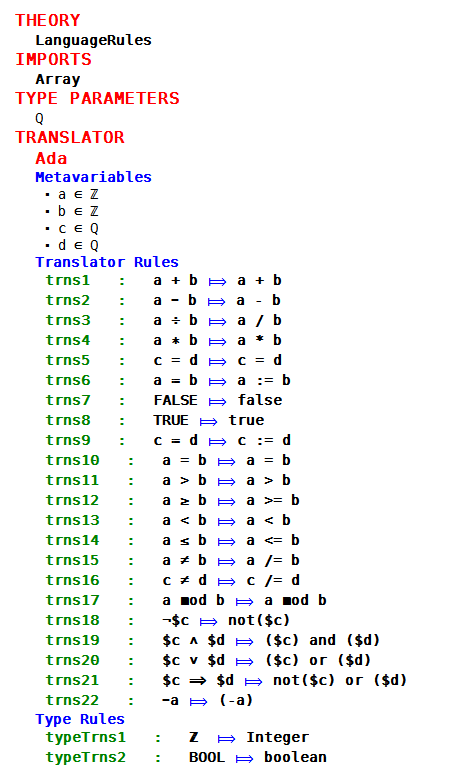
| | + | The theory plug-in is used to add mathematical extensions to Rodin. The theories are created, and deployed, and can then be used in any models in the workspace. When dealing with implementation level models, such as in Tasking Event-B, we need to consider how to translate newly added types and operators into code. We have augmented the theory interface with a Translation Rules section. This enables a user to define translation rules that map Event-B formulas to code. |
| | + | === Translation Rules=== |
| | + | Figure 1 shows the interface, and some translations rules of the mapping to Ada. |
| | | | |
| − | The Event-B XText front-end provides text editors for XContexts and and XMachines which then compiled automatically to Event-B contexts and machines.<br>
| + | <div id="fig:Translation Rules"> |
| − | For more details about the principles of this editor, see [[Event-B_XText_Front-end|the Event-B XText Front-end page]].<br>
| + | <br/> |
| | + | [[Image:TheoryCGRules.png|center||caption text]] |
| | + | <center>'''Figure 1''': Translation Rules</center> |
| | + | <br/> |
| | + | </div> |
| | | | |
| − | == Installation ==
| + | The translation rules are templates used for pattern matching. The meta-variables are defined and typed, and used in the rules. Event-B expressions and predicates are defined on the left hand side of the rule, and the code to be output (as text) appears on the right hand side of the matching rule. |
| − | | |
| − | === Setup ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Before install the Event-B XText front-end, you need to add the XText update site (http://download.eclipse.org/modeling/tmf/xtext/updates/composite/releases/) as an additional software site.
| |
| − | * The Event-B XText front-end is available as a separate plug-in from the main Rodin update site (under 'Editors' category)
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Release Notes ===
| |
| − | See [[Event-B_XText_Front-end_Release_Notes | Event-B XText Front-end Release Notes]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | === IMPORTANT ===
| |
| − | * Currently, Event-B XText front-end ONLY supports "standard" Event-B machines and contexts.
| |
| − | * Since the XContexts and XMachines are compiled to the Rodin files, the corresponding Rodin contexts and machines will be '''OVER-WRITTEN'''. Any changes in the Rodin files will not be lost.
| |
| − | * '''DO NOT USE''' the Event-B XText Front-end if you use modelling plug-ins such as iUML-B state-machines and class-diagrams, as the additional modelling elements will be over-written.
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Configuration ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Event-B Explorer ===
| |
| − | By default, XContext files (extension ''bucx'') and XMachine files (extension ''bumx'') are not display in the ''Event-B Explorer''. To enable this, select ''Customize view'' for ''Event-B Explorer'' and uncheck the option ''All files and folders''.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | == Editing ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | === XContext ===
| |
| − | * Any file with extension ''*.bucx'' will be recognised as XContext file. As a result, XContext file can be created by the standard ''New File'' wizard of Eclipse.
| |
| − | * The XText syntax of XContext file is as follows.
| |
| − | XContext returns econtext::Context:
| |
| − | {econtext::Context}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT | SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | 'context' name=ID
| |
| − | ('extends' extends+=[econtext::Context]+)?
| |
| − | ('sets' sets+=XCarrierSet+)?
| |
| − | ('constants' constants+=XConstant+)?
| |
| − | ('axioms' axioms+=XAxiom+)?
| |
| − | 'end'
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XCarrierSet returns econtext::CarrierSet:
| |
| − | {econtext::CarrierSet}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT | SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=ID
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XConstant returns econtext::Constant:
| |
| − | {econtext::Constant}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT | SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=ID
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XAxiom returns econtext::Axiom:
| |
| − | {econtext::Axiom}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT | SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=XLABEL predicate=STRING (theorem?='theorem')?
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | terminal XLABEL returns ecore::EString:
| |
| − | '@' !(':')+ ':'
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − | | |
| − | === XMachine ===
| |
| − | * Any file with extension ''*.bumx'' will be recognised as XMachine file. As a result, XMachine file can be created by the standard ''New File'' wizard of Eclipse.
| |
| − | * The XText syntax of XMachine file is as follows.
| |
| − | XMachine returns emachine::Machine:
| |
| − | {emachine::Machine}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | 'machine' name=ID
| |
| − | ('refines' refines+=[emachine::Machine])?
| |
| − | ('sees' sees+=[econtext::Context]+)?
| |
| − | ('variables' variables+=XVariable+)?
| |
| − | ('invariants' invariants+=XInvariant+)?
| |
| − | ('variant' variant=XVariant)?
| |
| − | ('events' events+=XEvent (';' events+=XEvent)*)?
| |
| − | ('end')
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XVariable returns emachine::Variable:
| |
| − | {emachine::Variable}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=ID
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XInvariant returns emachine::Invariant:
| |
| − | {emachine::Invariant}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=XLABEL predicate=STRING (theorem?='theorem')?
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | terminal XLABEL returns ecore::EString:
| |
| − | '@' !(':')+ ':'
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XVariant returns emachine::Variant:
| |
| − | {emachine::Variant}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | expression=STRING
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XEvent returns emachine::Event:
| |
| − | {emachine::Event}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=ID
| |
| − | (
| |
| − | (extended?='extended')? &
| |
| − | (convergence=XConvergence)?
| |
| − | )
| |
| − | ('refines' refines+=[emachine::Event]+)?
| |
| − | (
| |
| − | ('with' witnesses+=XWitness+)?
| |
| − | 'begin'
| |
| − | actions+=XAction+
| |
| − | 'end'
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | 'when'
| |
| − | guards+=XGuard+
| |
| − | ('with' witnesses+=XWitness+)?
| |
| − | ('then'
| |
| − | actions+=XAction+)?
| |
| − | 'end'
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | 'any'
| |
| − | parameters+=XParameter+
| |
| − | 'where'
| |
| − | guards+=XGuard+
| |
| − | ('with' witnesses+=XWitness+)?
| |
| − | ('then'
| |
| − | actions+=XAction+)?
| |
| − | 'end'
| |
| − | )?
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | enum XConvergence returns emachine::Convergence:
| |
| − | ordinary = 'ordinary' | convergent = 'convergent' | anticipated = 'anticipated';
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XParameter returns emachine::Parameter:
| |
| − | {emachine::Parameter}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=ID
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XGuard returns emachine::Guard:
| |
| − | {emachine::Guard}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=XLABEL predicate=STRING (theorem?='theorem')?
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XWitness returns emachine::Witness:
| |
| − | {emachine::Witness}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=XLABEL predicate=STRING
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | XAction returns emachine::Action:
| |
| − | {emachine::Action}
| |
| − | (comment=(ML_COMMENT|SL_COMMENT))?
| |
| − | name=XLABEL action=STRING
| |
| − | ;
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Converting Rodin files to Event-B XText ==
| |
| − | Rodin contexts and machines can be converted to XContext and XMachine files using context menu. From the ''Event-B Explorer'', right click on a Rodin project, a Rodin context, or a Rodin machine will offer option ''Convert to XText''. When a Rodin project is selected, all Rodin contexts and machines within that project will be converted.
| |