Difference between pages "Extending the Static Checker" and "Extending the project explorer"
imported>Tommy m (→Processor) |
imported>Renato |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOCright}} | {{TOCright}} | ||
= Introduction = | = Introduction = | ||
| − | The purpose of this page is to describe how to extend the | + | The purpose of this page is to describe how to extend the Event-B project explorer. It covers on the one hand, the definition of the extension, and on the other hand its implementation. The Event-B project explorer is itself an implementation of the extension-point <tt>org.eclipse.ui.views</tt>. The corresponding view id is '''fr.systerel.explorer.navigator.view''' which is defined as a subclass of <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.CommonNavigator</tt> and it is over this view that we extend the project explorer. |
| − | The useful extension points are listed below; they offer the possibility to contribute to the | + | [[Image:EventB project explorer.png]] |
| − | * <tt>org. | + | |
| − | + | The useful extension points are listed below; they offer the possibility to contribute to the project explorer: | |
| − | * <tt>org. | + | * <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.navigatorContent</tt> |
| − | + | * <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.viewer</tt> | |
| − | |||
= Before Starting = | = Before Starting = | ||
| − | It is necessary to define the | + | It is necessary to define the elements and structure to be represented. We will use as an example the ''decompositionFile'' that is defined as follows: |
*decompositionFile | *decompositionFile | ||
**decompositionRoot | **decompositionRoot | ||
| − | ***Component ( | + | ***Component with the following attributes: ''machine'' (to be decomposed) |
| − | ***Configuration | + | ***Configuration with the following attributes: ''style'': shared event/shared variables; ''newProjectOption'': decompose in the same project/different projects; ''decomposeContextOption'': noDecomposition/minimal decomposition) |
| − | ***SubComponent (resulting decomposed parts) | + | ***SubComponent (resulting decomposed parts) with the following attributes: ''label'' |
| − | ****SubComponentElement (elements used to decompose: variables for shared event | + | ****SubComponentElement (elements used to decompose:variables for shared event and events for shared variable) with the following attributes: '' element name/identifier'' |
[[Image:Decomp file pretty print.png]] | [[Image:Decomp file pretty print.png]] | ||
| − | + | = Navigator Content = | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | A content extension provides a content and label provider that can be used by a navigator content service (in out case the ''Event-B project explorer''). The navigatorContent extension defines the specific classes for the content provider, label provider, and action provider in addition to the types of elements the extension knows about. To extend the project explorer, it is also required to add the following children of the navigatorContent: | |
| − | * | + | * ''triggerPoints'': defines the nodes to be used when resolving the Common Navigator content provider's getElements() or getChildren(). This is also used to select the extension for providing labels, images, descriptions and for sorting. |
| − | * | + | *''possibleChildren'': defines the node to be used when resolving the Common Navigator content provider's getParent(). It is also used to help determine the parent when handling drop operations. |
== Declaration == | == Declaration == | ||
| − | The | + | The navigatorContent extension-point allows tool writers to register their tool implementation under a symbolic name that is then used by the Rodin platform to find and run the tool. The symbolic name is the id of the tool extension. The declaration of this extension is defined as follows: |
| − | < | + | <!ELEMENT navigatorContent ((enablement | (triggerPoints , possibleChildren)) , actionProvider* , commonSorter* , override? , dropAssistant* , commonWizard*)> |
| − | + | <!ATTLIST navigatorContent | |
| − | + | id CDATA #REQUIRED | |
| − | + | name CDATA #REQUIRED | |
| − | + | priority (lowest|lower|low|normal|high|higher|highest) | |
| − | + | contentProvider CDATA #IMPLIED | |
| − | + | icon CDATA #IMPLIED | |
| − | + | activeByDefault (true | false) | |
| − | + | providesSaveables (true | false) | |
| − | + | labelProvider CDATA #IMPLIED | |
| − | + | > | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | A navigator content extension defines a content provider and label provider that can be used to provide children whenever an element matches the triggerPoints expression and also to provide a parent whenever an element matches the possibleChildren expression. Optionally, we may also provide an action provider which can provide menu contributions and action bar contributions when an element is selected that the extension contributed, or that matches the triggerPoints expression. It is possible to contribute with a sorter to sort elements that are contributed by the extension. | |
| − | The | + | * id - A unique ID to identify this extension. Used for extension activation and by other extensions that would like to extend the defined extension (e.g. add another <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.CommonActionProvider</tt>) |
| + | * name - Specify a display name for the Content Extension. The display name is used in the activation dialog to allow clients to turn an extension on or off. | ||
| + | * priority - Indicates the relative priority of this extension to other extensions. Used by the Common Navigator to handle sorting and organization of the contributed content from this extension in relation to content from other extensions. Defaults to "normal" | ||
| + | * contentProvider - Supplies the name of a class which implements <tt>org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ITreeContentProvider</tt> or <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.ICommonContentProvider</tt>. The content provider will be consulted when adding children to the tree. Use the enablement, triggerPoints, or possibleChildren clauses to indicate what kinds of content should trigger a request to your content provider. Elements contributed from the content provider are not guaranteed to appear in the tree in the same order. Clients should take advantage of the sorting extension (commonSorter) to ensure proper ordering of their elements. All elements contributed by this content provider are associated with this navigatorContent extension for the purposes of determining the label provider, action providers, sorters, drop assistants and common wizards. | ||
| + | * icon - A plugin-relative path to an icon for use when displaying the metadata about the content extension to the user. | ||
| + | * activeByDefault - Indicates whether the current extension will be active by default. Each content extension may be turned on or off by the user. The active state is differentiated from the visible state. See <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.viewer/viewerContentBinding</tt> for more information on visibility | ||
| + | *labelProvider - Supplies the name of a class which implements <tt>org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ILabelProvider</tt> or for more advanced functionality, the <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.ICommonLabelProvider</tt>. Clients may also implement <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.IDescriptionProvider</tt> in order to add text to the status bar at the bottom of the Eclipse workbench based on the selection in the viewer. Since Eclipse 3.4, clients may also implement <tt>org.eclipse.jface.viewers.DelegatingStyledCellLabelProvider.IStyledLabelProvider</tt> to provide styled text labels. Note that the empty styled string signals that the label provider does not wish to render the label. | ||
| − | == | + | ===Action Provider=== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Still inside the navigatorContent, it is possible to add the following: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <!ELEMENT actionProvider (enablement?)> | |
| − | + | <!ATTLIST actionProvider | |
| − | + | class CDATA #REQUIRED | |
| − | + | id CDATA #IMPLIED | |
| − | + | dependsOn CDATA #IMPLIED | |
| − | + | overrides CDATA #IMPLIED | |
| − | + | priority (lowest|lower|low|normal|high|higher|highest) | |
| − | + | appearsBefore IDREF #IMPLIED | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <!ELEMENT | ||
| − | <!ATTLIST | ||
| − | id CDATA # | ||
| − | |||
> | > | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | A top level actionProvider is visible to an abstract viewer if there is a viewerActionBinding for that actionProvider. It is possible to provide actionProvider(s) under the root extension element (peer to other navigatorContent) in order to better control their enablement and viewer binding (see viewerActionBinding). Any items contributed to the toolbar or the view menu should be removed when the actionProviders is disposed. We described the two most used attributes of this element: | |
| − | + | * ''class'' - Supplies the name of a class that implements <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.CommonActionProvider</tt>. The action provider has an opportunity to contribute to the context menu and the retargetable actions defined in the IActionBars for the view that holds the navigator. It is also possible to contribute directly to the view menu through the IActionBars view menu. | |
| − | + | * ''id'' - Clients may optionally define an id to use for filtering purposes (either through activities or viewerContentBindings). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | To define when to enable this actionProvider, it is necessary to define the ''enablement'': | |
| − | + | <!ELEMENT enablement (not , and , or , instanceof , test , systemTest , equals , count , with , resolve , adapt , iterate , reference)*> | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The enablement expression allows clients to specify the same expression for both triggerPoints and possibleChildren. In the case of actionProvider, clients must define an expression that will indicate to the framework when their <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.CommonActionProvider</tt> should be invoked. Because of contributions to the ''IActionBars'', clients must be invoked whenever an object they are interested in is selected. Therefore, clients should use discretion in deciding when their extension should be enabled. | |
== Programmatic usage == | == Programmatic usage == | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | In the java side, create 4 packages: | |
| − | |||
| − | + | * *.*.editors.image: Where you have the class that handles the images to be used to display the elements in the project explorer (see for example: <tt>/org.eventb.ui/src/org/eventb/ui/IEventBSharedImages.java</tt>) | |
| − | + | * *.*.ui.explorer.contentProvider: contains the classes required in the extension point <tt>org.eclipse.ui.navigator.navigatorContent</tt>. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * *.*.ui.explorer.actionProvider: contains the classes that handle the actions that can be originated by the added navigatorContent. | |
| − | * <tt> | + | * *.*.ui.explorer.model: The content of the explorer is structured in classes called ''Models''. They all implement the interface <tt>fr.systerel.internal.explorer.model.IModelElement</tt>. The elements are structured in projects (''ModelProjects'') where the root file contains elements that can have proof obligations associated (in that case they should extends the abstract class <tt>fr.systerel.internal.explorer.model.ModelPOContainer</tt>). The elements of a root file are ''ModelElementNode'' similar to <tt>fr.systerel.internal.explorer.model.ModelElementNode</tt>. The models structure would look like this: |
| − | + | ModelProject | |
| + | - ModelRoot1 | ||
| + | - ModelElementNode1 | ||
| + | - ModelElementNode2 | ||
| + | - ... | ||
| + | - ModelRoot2 | ||
| + | - ModelElementNode3 | ||
| + | - ModelElementNode4 | ||
| + | - ... | ||
| + | |||
| + | Moreover, a class called ''ModelController'' defined as a singleton controls all the models and contains useful methods. It also implements the interface <tt>org.rodinp.core.IElementChangedListener</tt> that will be called whenever there is a change in one of the model elements. It will clean up the existing elements in the project explorer and reload with the recent changes. The ''ModelController'' instance should be called by implementing the method <tt>org.eclipse.jface.viewers.IContentProvider#inputChanged</tt> (required for classes that implement interface <tt>org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ITreeContentProvider</tt>). Usually an abstract class that implements ITreeContentProvider is created: ''AbstractContentProvider''. | ||
| − | + | public abstract class AbstractContentProvider implements ITreeContentProvider { | |
| + | protected static Object[] NO_OBJECT = new Object[0]; | ||
| + | protected IInternalElementType<?> type; | ||
| + | public AbstractContentProvider(IInternalElementType<?> type){this.type = type;} | ||
| + | public Object[] getChildren(Object parentElement) { | ||
| + | IModelElement model = ModelControllerDecomposition.getModelElement(parentElement); | ||
| + | if (model != null) { | ||
| + | return model.getChildren(type, false); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | return NO_OBJECT; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | public Object getParent(Object element) { | ||
| + | IModelElement model = ModelControllerDecomposition.getModelElement(element); | ||
| + | if (model != null) { | ||
| + | return model.getParent(true); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | return null; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | public boolean hasChildren(Object element) { | ||
| + | return getChildren(element).length>0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | public Object[] getElements(Object inputElement) { | ||
| + | return getChildren(inputElement); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | public void dispose() {} | ||
| + | public void inputChanged(Viewer viewer, Object oldInput, Object newInput) { | ||
| + | if (viewer instanceof CommonViewer) { | ||
| + | ModelControllerDecomposition.createInstance((CommonViewer)viewer); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | This class is extended by the respective ''contentProviders''. For instance: | |
| − | + | public class DecompositionContentProvider extends AbstractContentProvider{...} | |
| − | + | == Example == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | An example of the implementation of this extension-point is defined below: | |
| − | + | <extension | |
| + | point="org.eclipse.ui.navigator.navigatorContent"> | ||
| + | <navigatorContent | ||
| + | contentProvider="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.contentProvider.DecompositionContentProvider" | ||
| + | id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.decomposition" | ||
| + | labelProvider="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.contentProvider.DecompositionLabelProvider" | ||
| + | name="Decomposition Root" | ||
| + | priority="highest"> | ||
| + | <triggerPoints> | ||
| + | <or> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="org.eclipse.core.resources.IProject"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionRoot"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | </or></triggerPoints> | ||
| + | <possibleChildren> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionRoot"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | </possibleChildren> | ||
| + | </navigatorContent> | ||
| + | <navigatorContent | ||
| + | contentProvider="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.contentProvider.ComponentContentProvider" | ||
| + | id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.component" | ||
| + | labelProvider="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.contentProvider.DecompositionLabelProvider" | ||
| + | name="Decomposition Component" | ||
| + | priority="higher"> | ||
| + | <triggerPoints> | ||
| + | <or> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionRoot"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IComponent"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | </or> | ||
| + | </triggerPoints> | ||
| + | <possibleChildren> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IComponent"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | </possibleChildren> | ||
| + | </extension> | ||
| − | + | Above we defined two navigatorContent elements (''DecompositionContentProvider'' and ''ComponentContentProvider'') using the same class as labelProvider (''DecompositionLabelProvider''). The first is triggered by instances of ''IProject'' and ''IDecompositionRoot'' and the possible children of this element are ''IDecompositionRoot'' as well. | |
| − | + | An actionProvider example is described below: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | <actionProvider |
| − | + | class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.actionProvider.DecompositionRootActionProvider" | |
| + | id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.DecompositionRootActionProvider"> | ||
| + | <enablement> | ||
| + | <or> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionRoot"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionConfiguration"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.ISubComponent"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.ISubComponentElement"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | <instanceof | ||
| + | value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IComponent"> | ||
| + | </instanceof> | ||
| + | </or> | ||
| + | </enablement> | ||
| + | </actionProvider> | ||
| − | + | This actionProvider, described by the class <tt>ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.actionProvider.DecompositionRootActionProvider</tt> is enabled by instances of IDecompositionRoot, IDecompositionConfiguration, ISubComponent, ISubComponentElement and IComponent. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | = Navigator Viewer = |
| + | The viewer element defines the configuration for a common viewer. The extension may provide a custom popup menu id, override whether the viewer provides link with editor support, provides a filter dialog, and/or provides an "Available customizations" dialog. In addition, nested configuration elements give full control over the structure and behavior of the popup context menu. We define two children of this extension point: | ||
| − | + | * viewerContentBinding: to define the visibility of ''contentProviders''. | |
| − | + | * viewerActionBinding: to define the visibility of ''actionProviders''. | |
| − | === | + | == Declaration == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <!ELEMENT | + | <!ELEMENT viewerContentBinding (includes? , excludes?)> |
| − | <!ATTLIST | + | <!ATTLIST viewerContentBinding |
| − | + | viewerId CDATA #REQUIRED | |
> | > | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Clients must define one or more viewerContentBinding elements to describe which content extensions, common filters, and link helpers are visible to the viewer. A content extension or common filter is visible if the id of the content extension or common filter matches an includes statement under a viewerContentBinding and is not excluded by an excludes statement. If a content extension or common filter is not visible to a viewer, then the extension will never be asked for content by a content service for that viewer or be presented to the user in the available filters dialog. Clients may define an includes element to select which extensions are visible to the viewer, and similarly an excludes element for extensions that should not be made visible to the viewer. Clients may further define the extensions that should be explicitly queried for root elements (through ITreeContentProvider.getElements()) by the "isRoot" attribute. If one or more contentExtension elements have "isRoot" set to true within the includes statement, only those extensions will be queried for root elements. The "isRoot" attribute has no effect for exclusions. A viewer may have multiple viewerContentBindings defined, and their includes/excludes statements will be aggregated to produce the final behavior. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * viewerId - The id of the common viewer. If the viewer is in a common navigator then the id must match the navigator's id defined in its org.eclipse.ui.views extension. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <!ELEMENT viewerActionBinding (includes? , excludes?)> | |
| − | + | <!ATTLIST viewerActionBinding | |
| − | + | viewerId CDATA #REQUIRED | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <!ATTLIST | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
> | > | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Clients must define which action providers are visible to their viewer. Clients may define an includes element to select which extensions are visible to the viewer, and similarly an excludes element for extensions that should not be made visible to the viewer. A viewer may have multiple viewerActionBindings defined, and their includes/excludes statements will be aggregated to produce the final behavior. | |
| − | + | == Example == | |
| − | + | An example of the use of this extension point is defined below: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <extension | |
| + | point="org.eclipse.ui.navigator.viewer"> | ||
| + | <viewerContentBinding | ||
| + | viewerId="fr.systerel.explorer.navigator.view"> | ||
| + | <includes> | ||
| + | <contentExtension | ||
| + | pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.decomposition"> | ||
| + | </contentExtension> | ||
| + | <contentExtension | ||
| + | pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.component"> | ||
| + | </contentExtension> | ||
| + | <contentExtension | ||
| + | pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.configuration"> | ||
| + | </contentExtension> | ||
| + | <contentExtension | ||
| + | pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.subComponent"> | ||
| + | </contentExtension> | ||
| + | <contentExtension | ||
| + | pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.subComponentElement"> | ||
| + | </contentExtension> | ||
| + | </includes> | ||
| + | </viewerContentBinding> | ||
| + | <viewerActionBinding | ||
| + | viewerId="fr.systerel.explorer.navigator.view"> | ||
| + | <includes> | ||
| + | <actionExtension | ||
| + | pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.DecompositionRootActionProvider"> | ||
| + | </actionExtension> | ||
| + | </includes> | ||
| + | </viewerActionBinding> | ||
| + | </extension> | ||
| − | + | The pattern correspond to the ids in the contentProvider and actionProvider extension-points defined above (see the navigatorContent example section). | |
| − | |||
[[Category:Developer documentation]] | [[Category:Developer documentation]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Rodin Platform]] |
Revision as of 16:12, 24 May 2010
Introduction
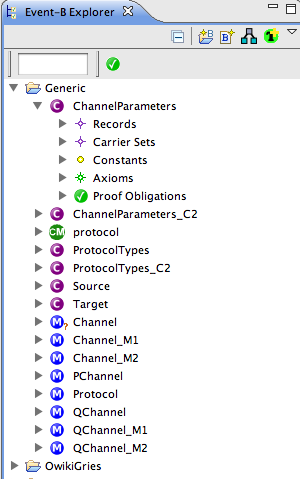
The purpose of this page is to describe how to extend the Event-B project explorer. It covers on the one hand, the definition of the extension, and on the other hand its implementation. The Event-B project explorer is itself an implementation of the extension-point org.eclipse.ui.views. The corresponding view id is fr.systerel.explorer.navigator.view which is defined as a subclass of org.eclipse.ui.navigator.CommonNavigator and it is over this view that we extend the project explorer.
The useful extension points are listed below; they offer the possibility to contribute to the project explorer:
- org.eclipse.ui.navigator.navigatorContent
- org.eclipse.ui.navigator.viewer
Before Starting
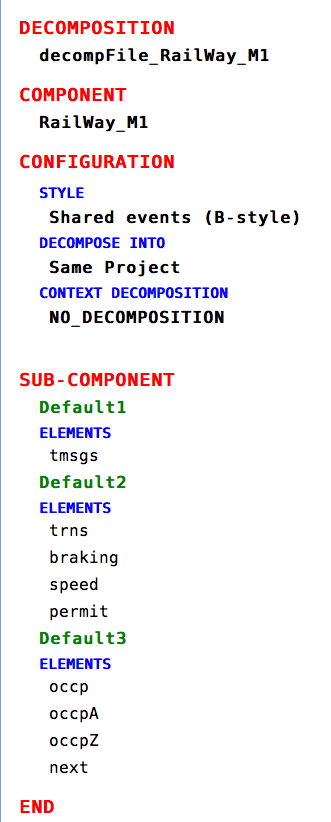
It is necessary to define the elements and structure to be represented. We will use as an example the decompositionFile that is defined as follows:
- decompositionFile
- decompositionRoot
- Component with the following attributes: machine (to be decomposed)
- Configuration with the following attributes: style: shared event/shared variables; newProjectOption: decompose in the same project/different projects; decomposeContextOption: noDecomposition/minimal decomposition)
- SubComponent (resulting decomposed parts) with the following attributes: label
- SubComponentElement (elements used to decompose:variables for shared event and events for shared variable) with the following attributes: element name/identifier
- decompositionRoot
A content extension provides a content and label provider that can be used by a navigator content service (in out case the Event-B project explorer). The navigatorContent extension defines the specific classes for the content provider, label provider, and action provider in addition to the types of elements the extension knows about. To extend the project explorer, it is also required to add the following children of the navigatorContent:
- triggerPoints: defines the nodes to be used when resolving the Common Navigator content provider's getElements() or getChildren(). This is also used to select the extension for providing labels, images, descriptions and for sorting.
- possibleChildren: defines the node to be used when resolving the Common Navigator content provider's getParent(). It is also used to help determine the parent when handling drop operations.
Declaration
The navigatorContent extension-point allows tool writers to register their tool implementation under a symbolic name that is then used by the Rodin platform to find and run the tool. The symbolic name is the id of the tool extension. The declaration of this extension is defined as follows:
<!ELEMENT navigatorContent ((enablement | (triggerPoints , possibleChildren)) , actionProvider* , commonSorter* , override? , dropAssistant* , commonWizard*)> <!ATTLIST navigatorContent id CDATA #REQUIRED name CDATA #REQUIRED priority (lowest|lower|low|normal|high|higher|highest) contentProvider CDATA #IMPLIED icon CDATA #IMPLIED activeByDefault (true | false) providesSaveables (true | false) labelProvider CDATA #IMPLIED >
A navigator content extension defines a content provider and label provider that can be used to provide children whenever an element matches the triggerPoints expression and also to provide a parent whenever an element matches the possibleChildren expression. Optionally, we may also provide an action provider which can provide menu contributions and action bar contributions when an element is selected that the extension contributed, or that matches the triggerPoints expression. It is possible to contribute with a sorter to sort elements that are contributed by the extension.
- id - A unique ID to identify this extension. Used for extension activation and by other extensions that would like to extend the defined extension (e.g. add another org.eclipse.ui.navigator.CommonActionProvider)
- name - Specify a display name for the Content Extension. The display name is used in the activation dialog to allow clients to turn an extension on or off.
- priority - Indicates the relative priority of this extension to other extensions. Used by the Common Navigator to handle sorting and organization of the contributed content from this extension in relation to content from other extensions. Defaults to "normal"
- contentProvider - Supplies the name of a class which implements org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ITreeContentProvider or org.eclipse.ui.navigator.ICommonContentProvider. The content provider will be consulted when adding children to the tree. Use the enablement, triggerPoints, or possibleChildren clauses to indicate what kinds of content should trigger a request to your content provider. Elements contributed from the content provider are not guaranteed to appear in the tree in the same order. Clients should take advantage of the sorting extension (commonSorter) to ensure proper ordering of their elements. All elements contributed by this content provider are associated with this navigatorContent extension for the purposes of determining the label provider, action providers, sorters, drop assistants and common wizards.
- icon - A plugin-relative path to an icon for use when displaying the metadata about the content extension to the user.
- activeByDefault - Indicates whether the current extension will be active by default. Each content extension may be turned on or off by the user. The active state is differentiated from the visible state. See org.eclipse.ui.navigator.viewer/viewerContentBinding for more information on visibility
- labelProvider - Supplies the name of a class which implements org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ILabelProvider or for more advanced functionality, the org.eclipse.ui.navigator.ICommonLabelProvider. Clients may also implement org.eclipse.ui.navigator.IDescriptionProvider in order to add text to the status bar at the bottom of the Eclipse workbench based on the selection in the viewer. Since Eclipse 3.4, clients may also implement org.eclipse.jface.viewers.DelegatingStyledCellLabelProvider.IStyledLabelProvider to provide styled text labels. Note that the empty styled string signals that the label provider does not wish to render the label.
Action Provider
Still inside the navigatorContent, it is possible to add the following:
<!ELEMENT actionProvider (enablement?)> <!ATTLIST actionProvider class CDATA #REQUIRED id CDATA #IMPLIED dependsOn CDATA #IMPLIED overrides CDATA #IMPLIED priority (lowest|lower|low|normal|high|higher|highest) appearsBefore IDREF #IMPLIED >
A top level actionProvider is visible to an abstract viewer if there is a viewerActionBinding for that actionProvider. It is possible to provide actionProvider(s) under the root extension element (peer to other navigatorContent) in order to better control their enablement and viewer binding (see viewerActionBinding). Any items contributed to the toolbar or the view menu should be removed when the actionProviders is disposed. We described the two most used attributes of this element:
- class - Supplies the name of a class that implements org.eclipse.ui.navigator.CommonActionProvider. The action provider has an opportunity to contribute to the context menu and the retargetable actions defined in the IActionBars for the view that holds the navigator. It is also possible to contribute directly to the view menu through the IActionBars view menu.
- id - Clients may optionally define an id to use for filtering purposes (either through activities or viewerContentBindings).
To define when to enable this actionProvider, it is necessary to define the enablement:
<!ELEMENT enablement (not , and , or , instanceof , test , systemTest , equals , count , with , resolve , adapt , iterate , reference)*>
The enablement expression allows clients to specify the same expression for both triggerPoints and possibleChildren. In the case of actionProvider, clients must define an expression that will indicate to the framework when their org.eclipse.ui.navigator.CommonActionProvider should be invoked. Because of contributions to the IActionBars, clients must be invoked whenever an object they are interested in is selected. Therefore, clients should use discretion in deciding when their extension should be enabled.
Programmatic usage
In the java side, create 4 packages:
- *.*.editors.image: Where you have the class that handles the images to be used to display the elements in the project explorer (see for example: /org.eventb.ui/src/org/eventb/ui/IEventBSharedImages.java)
- *.*.ui.explorer.contentProvider: contains the classes required in the extension point org.eclipse.ui.navigator.navigatorContent.
- *.*.ui.explorer.actionProvider: contains the classes that handle the actions that can be originated by the added navigatorContent.
- *.*.ui.explorer.model: The content of the explorer is structured in classes called Models. They all implement the interface fr.systerel.internal.explorer.model.IModelElement. The elements are structured in projects (ModelProjects) where the root file contains elements that can have proof obligations associated (in that case they should extends the abstract class fr.systerel.internal.explorer.model.ModelPOContainer). The elements of a root file are ModelElementNode similar to fr.systerel.internal.explorer.model.ModelElementNode. The models structure would look like this:
ModelProject
- ModelRoot1
- ModelElementNode1
- ModelElementNode2
- ...
- ModelRoot2
- ModelElementNode3
- ModelElementNode4
- ...
Moreover, a class called ModelController defined as a singleton controls all the models and contains useful methods. It also implements the interface org.rodinp.core.IElementChangedListener that will be called whenever there is a change in one of the model elements. It will clean up the existing elements in the project explorer and reload with the recent changes. The ModelController instance should be called by implementing the method org.eclipse.jface.viewers.IContentProvider#inputChanged (required for classes that implement interface org.eclipse.jface.viewers.ITreeContentProvider). Usually an abstract class that implements ITreeContentProvider is created: AbstractContentProvider.
public abstract class AbstractContentProvider implements ITreeContentProvider {
protected static Object[] NO_OBJECT = new Object[0];
protected IInternalElementType<?> type;
public AbstractContentProvider(IInternalElementType<?> type){this.type = type;}
public Object[] getChildren(Object parentElement) {
IModelElement model = ModelControllerDecomposition.getModelElement(parentElement);
if (model != null) {
return model.getChildren(type, false);
}
return NO_OBJECT;
}
public Object getParent(Object element) {
IModelElement model = ModelControllerDecomposition.getModelElement(element);
if (model != null) {
return model.getParent(true);
}
return null;
}
public boolean hasChildren(Object element) {
return getChildren(element).length>0;
}
public Object[] getElements(Object inputElement) {
return getChildren(inputElement);
}
public void dispose() {}
public void inputChanged(Viewer viewer, Object oldInput, Object newInput) {
if (viewer instanceof CommonViewer) {
ModelControllerDecomposition.createInstance((CommonViewer)viewer);
}
}
}
This class is extended by the respective contentProviders. For instance:
public class DecompositionContentProvider extends AbstractContentProvider{...}
Example
An example of the implementation of this extension-point is defined below:
<extension
point="org.eclipse.ui.navigator.navigatorContent">
<navigatorContent
contentProvider="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.contentProvider.DecompositionContentProvider"
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.decomposition"
labelProvider="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.contentProvider.DecompositionLabelProvider"
name="Decomposition Root"
priority="highest">
<triggerPoints>
<or>
<instanceof
value="org.eclipse.core.resources.IProject">
</instanceof>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionRoot">
</instanceof>
</or></triggerPoints>
<possibleChildren>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionRoot">
</instanceof>
</possibleChildren>
</navigatorContent>
<navigatorContent
contentProvider="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.contentProvider.ComponentContentProvider"
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.component"
labelProvider="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.contentProvider.DecompositionLabelProvider"
name="Decomposition Component"
priority="higher">
<triggerPoints>
<or>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionRoot">
</instanceof>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IComponent">
</instanceof>
</or>
</triggerPoints>
<possibleChildren>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IComponent">
</instanceof>
</possibleChildren>
</extension>
Above we defined two navigatorContent elements (DecompositionContentProvider and ComponentContentProvider) using the same class as labelProvider (DecompositionLabelProvider). The first is triggered by instances of IProject and IDecompositionRoot and the possible children of this element are IDecompositionRoot as well.
An actionProvider example is described below:
<actionProvider
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.actionProvider.DecompositionRootActionProvider"
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.DecompositionRootActionProvider">
<enablement>
<or>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionRoot">
</instanceof>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IDecompositionConfiguration">
</instanceof>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.ISubComponent">
</instanceof>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.ISubComponentElement">
</instanceof>
<instanceof
value="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.IComponent">
</instanceof>
</or>
</enablement>
</actionProvider>
This actionProvider, described by the class ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.explorer.actionProvider.DecompositionRootActionProvider is enabled by instances of IDecompositionRoot, IDecompositionConfiguration, ISubComponent, ISubComponentElement and IComponent.
The viewer element defines the configuration for a common viewer. The extension may provide a custom popup menu id, override whether the viewer provides link with editor support, provides a filter dialog, and/or provides an "Available customizations" dialog. In addition, nested configuration elements give full control over the structure and behavior of the popup context menu. We define two children of this extension point:
- viewerContentBinding: to define the visibility of contentProviders.
- viewerActionBinding: to define the visibility of actionProviders.
Declaration
<!ELEMENT viewerContentBinding (includes? , excludes?)> <!ATTLIST viewerContentBinding viewerId CDATA #REQUIRED >
Clients must define one or more viewerContentBinding elements to describe which content extensions, common filters, and link helpers are visible to the viewer. A content extension or common filter is visible if the id of the content extension or common filter matches an includes statement under a viewerContentBinding and is not excluded by an excludes statement. If a content extension or common filter is not visible to a viewer, then the extension will never be asked for content by a content service for that viewer or be presented to the user in the available filters dialog. Clients may define an includes element to select which extensions are visible to the viewer, and similarly an excludes element for extensions that should not be made visible to the viewer. Clients may further define the extensions that should be explicitly queried for root elements (through ITreeContentProvider.getElements()) by the "isRoot" attribute. If one or more contentExtension elements have "isRoot" set to true within the includes statement, only those extensions will be queried for root elements. The "isRoot" attribute has no effect for exclusions. A viewer may have multiple viewerContentBindings defined, and their includes/excludes statements will be aggregated to produce the final behavior.
- viewerId - The id of the common viewer. If the viewer is in a common navigator then the id must match the navigator's id defined in its org.eclipse.ui.views extension.
<!ELEMENT viewerActionBinding (includes? , excludes?)> <!ATTLIST viewerActionBinding viewerId CDATA #REQUIRED >
Clients must define which action providers are visible to their viewer. Clients may define an includes element to select which extensions are visible to the viewer, and similarly an excludes element for extensions that should not be made visible to the viewer. A viewer may have multiple viewerActionBindings defined, and their includes/excludes statements will be aggregated to produce the final behavior.
Example
An example of the use of this extension point is defined below:
<extension
point="org.eclipse.ui.navigator.viewer">
<viewerContentBinding
viewerId="fr.systerel.explorer.navigator.view">
<includes>
<contentExtension
pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.decomposition">
</contentExtension>
<contentExtension
pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.component">
</contentExtension>
<contentExtension
pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.configuration">
</contentExtension>
<contentExtension
pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.subComponent">
</contentExtension>
<contentExtension
pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.navigator.explorer.subComponentElement">
</contentExtension>
</includes>
</viewerContentBinding>
<viewerActionBinding
viewerId="fr.systerel.explorer.navigator.view">
<includes>
<actionExtension
pattern="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.ui.DecompositionRootActionProvider">
</actionExtension>
</includes>
</viewerActionBinding>
</extension>
The pattern correspond to the ids in the contentProvider and actionProvider extension-points defined above (see the navigatorContent example section).