Rewriting rules for event model decomposition: Difference between revisions
From Event-B
Jump to navigationJump to search
imported>Pascal |
imported>Pascal |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
* The <math>\bcmin</math> ("becomes member of") assignment is the set-based (non-deterministic) assignment, where a set expression is given for the assigned identifier. | * The <math>\bcmin</math> ("becomes member of") assignment is the set-based (non-deterministic) assignment, where a set expression is given for the assigned identifier. | ||
Let <math>v</math> and <math>w</math> be variables, and <math>E</math> and <math>F</math> be expressions. In the following table, the left-hand assignments are equivalent (\defi) to the right-hand ones: | Let <math>v</math> and <math>w</math> be variables, and <math>E</math> and <math>F</math> be expressions. In the following table, the left-hand assignments are equivalent (<math>\defi</math>) to the right-hand ones: | ||
{{SimpleHeader}} | {{SimpleHeader}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 07:53, 3 July 2009
The purpose of this page is to list and justify the rewriting / simplification rules applied in the event model decomposition when building the external events, and more especially their actions.
Rewriting rules for the Event-B assignments
As detailed in the modelling language, the Event-B assignments are formed of two parts:
- a left-hand side, which is a list of free identifiers.
- a right-hand side.
There are various kinds of assignments:
- The
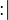 ("becomes such that") assignment is the most general (non-deterministic) assignment, where a predicate is given on the before and after values of assigned identifiers. The after values of the assigned identifiers are denoted by a primed identifier whose prefix is the assigned identifier.
("becomes such that") assignment is the most general (non-deterministic) assignment, where a predicate is given on the before and after values of assigned identifiers. The after values of the assigned identifiers are denoted by a primed identifier whose prefix is the assigned identifier. - The
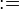 ("becomes equal to") assignment is the deterministic assignment where an expression is given for each assigned identifier.
("becomes equal to") assignment is the deterministic assignment where an expression is given for each assigned identifier. - The
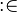 ("becomes member of") assignment is the set-based (non-deterministic) assignment, where a set expression is given for the assigned identifier.
("becomes member of") assignment is the set-based (non-deterministic) assignment, where a set expression is given for the assigned identifier.
Let 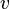 and
and 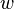 be variables, and
be variables, and 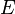 and
and 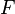 be expressions. In the following table, the left-hand assignments are equivalent (
be expressions. In the following table, the left-hand assignments are equivalent (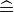 ) to the right-hand ones:
) to the right-hand ones:
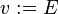 |
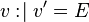
|
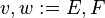 |

|
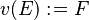 |
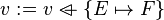
|
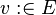 |
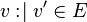
|
Thus, each Event-B assignment can be expressed in a "becomes such that" form.
Simplification rules on Event-B predicates
Rewriting rules for the Event-B actions
Let 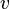 and
and 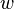 be variables, and
be variables, and 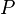 and
and 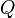 be predicates. The following rule applies :
be predicates. The following rule applies :
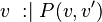 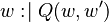 |
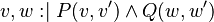
|