Constrained Dynamic Parser: Difference between revisions
imported>Mathieu |
imported>Mathieu |
||
| Line 294: | Line 294: | ||
A prototype as been developed in Python to quickly try different solutions. | A prototype as been developed in Python to quickly try different solutions. | ||
The development tree of the python prototype is available at http://bitbucket.org/matclab/eventb_pratt_parser/ with the ''default'' branch implementing a rather functionnal approach and the ''object'' | The development tree of the python prototype is available at http://bitbucket.org/matclab/eventb_pratt_parser/ with the ''default'' branch implementing a rather functionnal approach and the ''object'' branch being a first try to a more object based implementation. | ||
=== Tests === | === Tests === | ||
Revision as of 11:39, 5 February 2010
This page describes the requirements for a generic parser for the Event-B Mathematical Language.
A first design proposal is also drafted.
Requirements
In order to be usable mathematical extensions require that the event-b mathematical language syntax can be extended by the final user.
The lexical analyser and the syntaxic parser thus have to be extensible in a simple enough way (from a user point of vue).
Requirements Exported by the Current Language Design
Operator Priority
- operator are defined by group,
- group of operator have a defined precedences,
- there may be precedences defined inside groups.
Operator Compatibility
- a compatibility table defines allowed associativities inside a group,
- a compatibility table defines allowed associativities between groups (it allows to forbid a syntaxic construction like
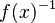 )
)
- nota: this requirement was added afterwards with consistency in mind.
Expected Extension Schemes
We do want to at least define operators of the following form :
- infix :
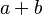 or
or 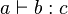
- prefix :
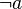
- postfix :
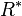
- closed :
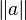
- parentheses sugar :
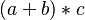
- functional postfix :
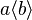
- functional prefix :
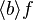
- lambda like :
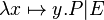
- Union like :
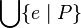 or
or 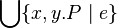
- sets :
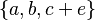 or
or 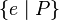 or
or 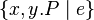
We also like to define precisely precedences and associativity between existing and new operators.
Requirements exported by the dynamic feature
- the precedence should not be enumerated, which would hinder extensibility, but defined by a relation, like: '+' < '*' and '*' < '**', ...
Limitations
TODO: explicit them
Design Alternatives
Three design alternatives where identified:
Make Existing Parser Extensible
The existing parser is a LL recursive descent parser generated by the Coco/R Compiler Generator, which makes extensive use of pre-computed lookahead, which makes it very difficult to be transformed in a parser witgh enough extensibility.
Parser Combinator
- on wikipedia. Some implementations are referenced here.
- with functionnal language Agda : Parsing Mixfix Operators
- This paper is interesting in its proposal of using an acyclic graph to define operator precedence.
- with functional language OPAL : How To Obtain Powerful Parsers That Are Elegant and Practical
Pratt Parser
Note that a pratt parser is essentially a parser for expressions (where expression parts are themselves expressions)... But it may be tweaked to limit the accepted sub-expressions or to enforce some non-expression parts inside an expression. More on that hereafter.
Some Existing Extensible Languages
- Katahdin, and the associated paper A Programming Language Where the Syntax and Semantics Are Mutable at Runtime which describes the language and its implementation (in C#).
- XMF whose implementation seems not be describes in details.
- XLR: Extensible Language and Runtime, which looks like a pratt parser according to the sources.
 whose implementation seems not be describes in details (but source code is available).
whose implementation seems not be describes in details (but source code is available).
Design Proposal
The chosen design is based on Pratt parser and is explained hereafter.
Main Concepts
- symbol
- a symbol is a lexem (finite,
 , ...)or a lexem class (number, identifier) known by the parser.
, ...)or a lexem class (number, identifier) known by the parser.
- group
- each symbol belongs to one and only one group (binary relation, assignment substitution,...).
- symbol compatibility
- a relation telling if inside a group two symbol are compatibles.
- Two symbol are compatibles is they can be parsed without parentheses (see Event-B Mathematical Language for more on compatibility).
- group compatibility
- a relation telling if two groups are compatibles.
- Two symbol of different groups are said compatibles if their group are compatibles.
- symbol associativity
- a relation which gives the associative precedence of symbols inside a given group.
- group associativity
- a relation which gives the associative precedence of groups.
- Two symbol of different groups have a relative precedence given by the associative precedence of their groups.
- generic parser
- the parser which is defined.
- This parser may be called recursively (an infix expression being build upon a left and right sub-expression) and is often the default parser used when building the AST associated with a symbol.
- specific parser
- some specific parser, predefined as helper functions to build specific AST.
Proposed User Interface
The hereafter proposition does not preclude the final UI from taќing other (more user friendly) form). But the concepts should probably stay the same
We propose that the user will be able to create several predefined type of symbols (new types may certainly be further added by mean of eclipse extension points). When defining a symbol, the user can choose the parser used to parse the sub-expressions (default to generic parser, but a specific parser may be used) and can enforce the form of the resulting parsed sub-expression in terms of their AST root type.
Predefined Symbol Builders
The proposed predefined symbol builders are:
- infix
- For example predicate conjunction which expects two predicates for left and right parts may be defined by
infix("∧", gid="(logic pred)", expected_nonterm=["predicate", "predicate"]), saying that '∧' is an operator belonging to the logic predicate group which accept a predicate on left and right. - As another example, substitution :∣ of group '(infix subst)' which expect one ident list for left term and and a predicate for the right one may be defined by
infix(":∣", "(infix subst)", expected_nonterm=["ident_list", "predicate"])
- prefix
prefix("¬", "(not pred)", expected_nonterm=["predicate"])
- atomic
atomic("⊤", "(atomic pred)")
- prefix closed
- used to build prefix symbol which must be followed by enclosing symbol(brackets, parentheses,..). For example finite may be defined by:
prefix_closed("finite", "(", ")","(atomic pred)", expected_nonterm=["expression"])
- postfix;
postfix("∼", gid="(unary relation)", expected_nonterm=["expression"])
- quantified
quantified("∀", "·", expected_nonterm=["predicate"]
- lambda like
lambda_like("λ", "·", u"∣", gid="(quantification)", expected_nonterm=["ident list", "predicate", "expression"])
- quantified union like
Union_like("⋃", "·", "∣", gid="(quantification)")
- closed sugar
- use for parentheses added to enforce associativity:
closed_sugar("(", ")")
- functional postfix
functional_postfix("(", ")", gid="(functional)", expected_nonterm=["expression", "expression"])
Some right associative versions of those symbol builders may also be supplied (infix_right, or a specific parameter right associative parameter may also be provided to the infix symbol builder).
Predefined Specific Parser
- expression lists
- ident lists
- maplet tree (for lambda)
Defining Compatibility and Precedences
Inside a group, compatibility may be defined like:
g = group["(binop)"]
g.add_many_compatibility(
[ ("∪", "∪"),
("∩", "∩"),
("∩", "∖"),
("∩", "▷"),
("∩", "⩥"),
("∘", "∘"),
(";", ";"),
(";", "▷"),
(";", "⩥"),
("", ""),
("◁", "∩"),
("◁", "∖"),
("◁", ";"),
("◁", "⊗"),
("◁", "▷"),
("◁", "⩥"),
("⩥", "∩"),
("⩥", "∖"),
("⩥", ";"),
("⩥", "⊗"),
("⩥", "▷"),
("⩥", "⩥"),
("×", "×"), ]
which defines the compatibility table for expression binary operator as defined in Event-B Mathematical Language.
Inside a group, precedence may be defined like:
g = group["(arithmetic)"]
g.add_many_precedence(
[ ("^", "÷"),
("^", "∗"),
("^", "+"),
("^", "−"),
("^", "mod"),
("+", "∗"),
("−", "∗"),
("+", "÷"),
("−", "÷"),
("+", "mod"),
("−", "mod"), ] )
which defines ^ as having the least precedence amongst the operators of the expression arithmetic group.
Similarly, precedences and compatibilities between groups may be defined :
group_precedence.add(("(binop)", "(interval)"))
group_precedence.add(("(interval)", "(arithmetic)"))
group_precedence.add(("(arithmetic)", "(unary relation)"))
group_precedence.add(("(unary relation)", "(bound unary)"))
group_precedence.add(( "(bound unary)", "(bool)"))
group_compatibility.add_all( [ "(binop)", "(interval)", (arithmetic)", "(unary relation)", "(unary relation)", "(bound unary)",....])
Some Difficulties
Some difficulties appear when trying to implement an Event-B parser with the preceding scheme:
- A symbol may be declared by several different builders (think of unary and infix minus for example).
- Pratt parsers are able to cope with a symbol appearing either at the beginning of an expression or inside an expression (see led and nud hereafter). For example, unary minus and infix minus can be both defined by the proposed scheme. However, in their default form, pratt parser failed in parsing symbol like '{' which appears at the beginning of extension sets, comprehension sets and quantified sets.
- SOLUTION #1: The existing Event-B parser uses an infinite lookahead to determine which one of those three sets is actually being parsed.
- This solution hinders the extensibility of the parser, because the addition of a symbol requires to modify the lookahead.
- However, such an issue may be bypassed, at least in a first version, in enforcing some usage rules. Thus, a new symbol contributed by an extension but used in the lookahead may be rejected as in invalid symbol.
- SOLUTION #2: Implementing a backtracking parser.
- More precisely, it means that the three sets are attempted to be parsed. The parsing is successful if and only if one of these attempts lead to a result (i.e., it is a failure if several attempts or none lead to a result).
- It is a good solution provided that we use memorisation to alleviate the cost of parsing formulas that require heavy backtracking.
- Some binary infix operators are in fact parsed as n-ary operators (with more than 2 childrens if possible).
- An attribute is required to specify if an operator shall be flattened (i.e., parsed as an n-ary operator) or not. It is indeed impossible to "deduce" this information (e.g., the minus operator, which is left associative and self-compatible, shall not be flattened).
- The flattenning should then be done by the parser associated to every symbol.
- The returned parsing errors shall be meaningful for users (e.g., the "Missing parenthesis" message may help to solve the problem when the "Invalid expression" message is too imprecise) TODO: how does it impact actual design?.
- Defining a grammar or a grammar extension is not an easy job, even with those simple mechanisms.
- It would certainly be a good idea to implement a user interface to test the grammar, so that an extension designer has a way to ensure that he agrees with the parser on the semantic of his extension (or at least on the AST obtained by using it). For example, the representation of the syntax tree returned by Formula.getSyntaxTree could be compared to an expected entered string.
Core Algorithm
Rough description
The algorithm is based on a table, associating a SymbolParser for each known operator (or lexem class). The MainParser then constructs the AST by using the led or nud parser instance attach to each symbol, taking into account symbol afformations such as group and precdenced for constructing the resulting AST.
Each led or nud parser instance may in turn make recursive calls to either the standard MainParser or to ad-hoc parsers. The choice of the subparsers used is given when the SymbolParser is created. TODO: complete?
Main Objects
- KnownSymbols
- a table associating a SymbolParser for each known symbol.
- SymbolParser
- a Parser for a specific symbol. It should at least have the following attributes:
- Array<LedParser> ledfor parsing the expression associated to the symbolidwhen it appears in the middle of an expression (left denotation)
- Array<NudParser> nudfor parsing the expression associated to the symbolidwhen it appears at the beginning of an expression (null denotation)
- String id
- String giddesigning the group to which theidsymbol belongs to.
- Array<LedParser>
- Note that parsers in led (respectively nud) will be tried one after another (with backtracking to the original state in between). If several of them succeed, an error is returned to the user, else the AST generated by the only one succeeding is returned.
- Parser
- A parser, which should have the following attributes
- Parser Array subparsersan array of subparsers used by theparsemethod. They defaults toMainParser, but may be set to specific parsers.
- Parser Array
- and the following methods:
- parse: this method should consume tokens and returns an AST. It may use severalsubparsers.
- ParserBuilder
- the class that inherited from this class provide the interface used to create new symbols. It has the following method:
- build: which build a SymbolParser and store it in the KnownSymbols container as being associated to the symbol for which the parser is being built.
- MainParser
- This class inherits from Parser and its parsefunction implements the core of the pratt algorithm.
- Without taking into account backtracking, the algorithm reads:
def parse(reckognized_token, has_right_associativity=False):
global token
t = token # t is the processed symbol
token = tokenizer.next() # token is the next symbol
left = t.nud() # a new expression is being parsed (null denotation : nothing on the left)
while has_less_priority(reckognized_token, token, has_right_associativity):
t = token
token = next_token() # if precedence allows it, we parse next expression
left = t.led(left) # has being left expression of current symbol (left denotation)
return left
- The parsing of a new expression is initiated by:
token = tokenizer.next()
ast = MainParser.parse(KnownSymbols["(eof)"])
- where the tokenizerreturns the SymbolParser associated to the next lexem.
- identListParser
- inherits from Parser. Its parsefunction implements the parsing of an ident list (like
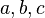 ).
). - identMapletListParser
- inherits from Parser . Its parsefunction implements the parsing of a maplet list as used in lambda expression (like
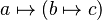 ).
). - expressionListParser
- inherits from Parser . Its parsefunction implements a list of expression as used in the extension set expression.
TODO: section being worked on
- infixParser
- inherits from Parser. Its parsefunction is a led parser and implements something like (pseudocode):
parse(AST left):
ast = new AST()
ast.first = left
verify_expected_group(ast.first, this.expected_non_terminals[0])
ast.second = this.parsers[0].parse(ast, is_right_associative=False)
verify_expected_group(ast.second, this.expected_non_terminals[1])
return ast
- infixBuilder
- inherits from ParserBuilder and has the following methods:
build(Lexem lexem, GroupID gid, Array<Parser> parsers, Array<NonTermGroups> expected_non_terminals)which implements something like:
if lexem in KnownSymbols:
else:
TODO
Open Questions
How does the user specify the expected AST?
- Some examples in the existing parser:
- Bound identifiers are converted to de Bruijn indexes while constructing the AST. Is this desirable ? How does the user specify that identifier are bound or not ?
Sample Implementation
A prototype as been developed in Python to quickly try different solutions.
The development tree of the python prototype is available at http://bitbucket.org/matclab/eventb_pratt_parser/ with the default branch implementing a rather functionnal approach and the object branch being a first try to a more object based implementation.
Tests
- Regression tests. The tests of the existing parser shall succeed when applied to the generic parser.
- New tests.