Event Model Decomposition: Difference between revisions
imported>Pascal |
imported>Pascal |
||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
===== The initialization event ===== | ===== The initialization event ===== | ||
<font size color="red"> | <font size color="red">What about the initialization event?</font> | ||
==== About the invariants ==== | ==== About the invariants ==== | ||
Revision as of 09:09, 25 June 2009
Introduction
One of the most important feature of the Event-B approach is the ability to introduce new events during refinement steps, but a consequence is an increasing complexity of the refinement process when having to deal with many events and many state variables.
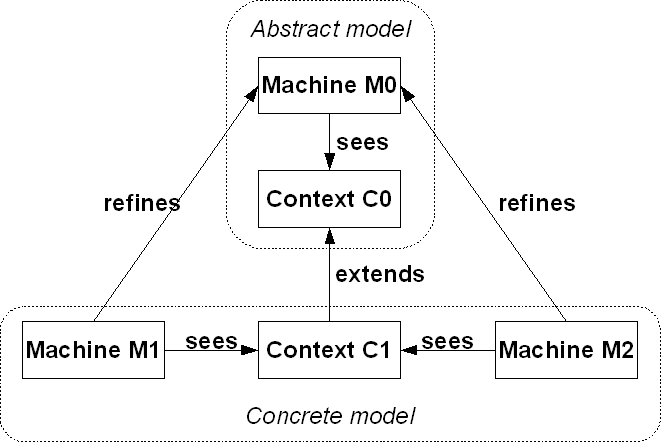
The main idea of the decomposition is to cut a model 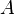 into sub-models
into sub-models 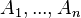 , which can be refined separately and more confortably than the whole.
, which can be refined separately and more confortably than the whole.
The constraint that shall be satisfied by the decomposition is that these refined models might - the recomposition will never be performed in practice - be recomposed into a whole model 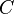 in a way that guarantees that
in a way that guarantees that 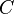 refines
refines 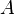 . An event-based decomposition of a model is detailed in Event Model Decomposition: the events of a model are partitioned to form the events of the sub-models. In parallel, the variables on which these events act are distributed among the sub-models.
. An event-based decomposition of a model is detailed in Event Model Decomposition: the events of a model are partitioned to form the events of the sub-models. In parallel, the variables on which these events act are distributed among the sub-models.
The purpose is here to precisely describe what is required at the Rodin platform level to integrate this event model decomposition, and to explain why. The details of how it could be implemented are out of scope.
Terminology
- Event model decomposition: The decomposition of a model, as defined in the modelling language, in sub-models.
A model can contain contexts, machines, or both. The events are contained in the machines, as well as the variables on which they act, the invariants constraining these variables, and optionnally the variants. The notion of model decomposition is then an extrapolation for the notion of machine decomposition.
- Shared variable: A variable of a given model which is accessed (read/written) by several distinct events (by opposition to private variable).
- Private variable: A variable of a given model which is only accessed by an event (by opposition to shared variable).
- External event: An event of a sub-model simulating the way the read (but not written) variables of a sub-model are handled in the initial model.
Architecture
Specification
High-level requirements
- Configuring the decomposition
- Identifying the machine to be decomposed
- Identifying the sub-machines to be created
- Specifying how to perform the decomposition (event partition)
- Asking for simplifications
- Performing the decomposition
- Generating the sub-machines
- Linking the sub-machines to the initial machine
- Generating the sub-contexts
- Linking the sub-contexts to the sub-machines
- Generating the useful proof obligations
- Not "propagating" useless proof obligations
- Checking the decomposition
Low-level requirements
About the variables
Some variables are needed by several sub-machines of the decomposition. As a consequence, these variables shall be replicated in the sub-machines. Beyond that, since it is not possible to ensure that such a variable will be refined in the same way in each sub-machine, they shall be given a special status (shared variable), with the limitation that they cannot be refined.
We will specify in this section how to introduce the notion of shared variable in the Rodin platform, and how to check the associated rules.
The following DTD excerpt describes the structure of a variable in the Rodin database:
<!ENTITY % NameAttDecl "name CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ENTITY % CommentAttDecl "org.eventb.core.comment CDATA #IMPLIED"> <!ENTITY % IdentAttDecl "org.eventb.core.identifier CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ELEMENT %variable; EMPTY> <!ATTLIST %variable; %NameAttDecl; %CommentAttDecl; %IdentAttDecl; >
A first possibility to tag a variable as shared would be to add a shared specific attribute, which would be set to true if and only if the variable is shared:
<ENTITY % shared "org.eventb.core.shared CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ELEMENT %variable; EMPTY> <!ATTLIST %variable; ... %shared; (false|true) #REQUIRED >
Another possibility would be to define a more generic attribute, which could take different values, according to the nature of the variable:
<ENTITY % nature "org.eventb.core.nature CDATA #REQUIRED">
<!ATTLIST %variable;
...
%nature; (0|1) #REQUIRED
>
<!-- The nature attribute encodes the kind of variable:
0: ordinary variable
1: shared variable
-->
The second option, which has the main advantage to be more evolutive, is retained here.
A shared variable shall always be present in the state space of any refinement of the component. The verification shall be added to those already performed by the static checker.
Partitionning the variables in the sub-components of the decomposition
TODO
About the events
It shall be possible to simulate the way the shared variables are handled in the non-decomposed machine. This is precisely the purpose of the so-called external events.
We will examine in this section how to define such events in the Rodin platform, how to construct them, and how to enforce the rules that apply (in particular, these events cannot be refined).
Identifying an event as external
An attribute is already defined, which is introduced below, to precise the nature of an event. A first solution would be to add another masked value (eg. 4) to encode the external status.
<!ENTITY % convergence "org.eventb.core.convergence">
<!ATTLIST %event;
...
%convergence; (0|1|2) #REQUIRED
...
>
<!--
The convergence attribute specifies which PO should be generated
for the combination event / variant:
0: ordinary event, no PO
1: convergent event, PO to show event decreases variant
2: anticipated event, PO to show event doesn't increase variant
-->
Another solution would be to add a distinct external attribute, which would be set to true if and only if the event is external:
<ENTITY % external "org.eventb.core.external CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ATTLIST %event; ... %external; (false|true) #REQUIRED >
This solution is preferred because the notion of external event is totally orthogonal to the notion of convergence.
Constructing an external event
An external event shall be built for each event of the non-decomposed machine modifying shared variables.
As explained in the modelling language, a non-deterministic action expressed as a variable identifier, followed by 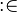 , followed by a set expression, can always be translated to a non-deterministic action made of a list of distinct variable identifiers, followed by
, followed by a set expression, can always be translated to a non-deterministic action made of a list of distinct variable identifiers, followed by 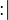 , followed by a before-after predicate.
, followed by a before-after predicate.
In the same manner, a deterministic action can always be translated to a non-deterministic action, as shown in the following example. Let's consider a machine with variables 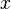 , and
, and 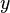 . Here is an action:
. Here is an action:
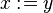 is the same as is the same as 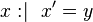
|
As a consequence, we will focus on the construction of an external event from an event whose action relies on 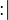 . The construction is illustrated with the following example, where
. The construction is illustrated with the following example, where  is an event,
is an event, 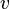 is an ordinary (i.e. it is not shared) variable,
is an ordinary (i.e. it is not shared) variable,  is a shared variable,
is a shared variable, 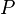 is a before-after predicate, and
is a before-after predicate, and 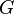 is a predicate.
is a predicate.
e WHERETHEN
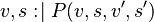
The first step of the construction is to replace the ordinary variable by a parameter. Note that this step is purely fictive, because assigning an event parameter is not allowed!
e ANYWHERE
THEN
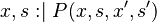
The second step of the construction is to introduce an existantial quantifier to resolve the invalid assigment. 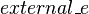 is the newly built external event.
is the newly built external event.
external_e ANYWHERE
THEN
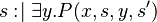
- Should deterministic actions and other non-deterministic actions be handled specifically?
Eg1. Proof obligations generated for deterministic actions seem more suitable than those generated for non-deterministic actions.
Eg2. In the same manner, for a given set 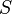 , proving that
, proving that 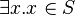 (
(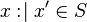 ) is not as simple as proving that
) is not as simple as proving that 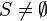 (
(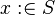 ).
).
- How many external events should be built from an event modifying several shared variables? One per shared variable?
- What should be performed if it is necessary to add an additional guard in order to define the type of a parameter?
Partitionning the events in the sub-components of the decomposition
It is assumed in this section that the variables have been previously partitionned among the sub-machines.
The following cases have then to be taken into consideration when dealing with the partitionning of the events:
- Case 1: If
 is an event that only accesses in write mode a private variable
is an event that only accesses in write mode a private variable 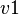 , then
, then  shall be deplaced in the sub-machine containing
shall be deplaced in the sub-machine containing 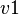 .
. - Case 2: If
 is an event that both accessed in write mode a private variable
is an event that both accessed in write mode a private variable 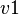 and a shared variable
and a shared variable 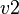 , then
, then  shall be deplaced in the sub-machine that contains
shall be deplaced in the sub-machine that contains 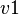 . Moreover, an external event that modifies
. Moreover, an external event that modifies 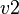 shall be built and duplicated in each sub-machine where
shall be built and duplicated in each sub-machine where 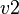 is only read.
is only read. - Case 3: If
 is an event that only accesses in write mode a shared variable
is an event that only accesses in write mode a shared variable 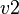 , then
, then  can be equally deplaced in a sub-machine containing
can be equally deplaced in a sub-machine containing 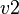 . An external event that modifies
. An external event that modifies 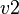 shall be built and duplicated in other sub-machines where
shall be built and duplicated in other sub-machines where 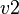 is only read.
is only read.
Is the user asked to indicate its choice in case 3?
Should the external event be duplicated in each sub-machine where the shared variable is used (i.e. is read or written)?
Ensuring that an external event cannot be refined
The verification shall be performed by the static checker.
The initialization event
What about the initialization event?
About the invariants
- Copying an invariant dealing with the private variables of a sub-component in the sub-component
- Copying an invariant involving a shared variable only in the sub-components where this variable is shared
- Not copying an invariant related to private and shared variables (?)
About the variants
About the contexts
- Linking the sub-contexts
Bibliography
- J.R. Abrial, Mathematical Models for Refinement and Decomposition, in The Event-B Book, to be published in 2009 (lien externe).
- J.R. Abrial, Event Model Decomposition, Version 1.3, April 2009.
- M. Butler, Decomposition Structures for Event-B, in Integrated Formal Methods iFM2009, Springer, LNCS 5423, 2009 (lien externe).