MBT plugin: Difference between revisions
imported>LaurentiuMM No edit summary |
imported>LaurentiuMM No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|} | |} | ||
MBT (Model- | '''MBT (Model-Based Testing) for Event-B plugin''' | ||
==Installing == | ==Installing == | ||
The MBT plugin relies on Rodin release 2.0 or newer and ProB plugin 2.2 or newer. | |||
The MBT for Event-B plugin (also referred to as MBT plugin) relies on Rodin release 2.0 or newer and ProB plugin 2.2 or newer. | |||
The following steps will guide you through the installation process: | The following steps will guide you through the installation process: | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
===Short theoretical aspects=== | ===Short theoretical aspects=== | ||
The MBT for Event-B plugin iteratively constructs a subset of the ''state space'' of an Event-B model (which is essentially an ''abstract state machine'' where the states can be implicitly derived from the values of the model variables), together with an associated ''test suite'', using an ''incremental model learning'' which keeps under control the ''state space explosion''. In the following, we will refer to this process as the Learn DFCA algorithm. | The MBT for Event-B plugin iteratively constructs a subset of the ''state space'' of an Event-B model (which is essentially an ''abstract state machine'' where the states can be implicitly derived from the values of the model variables), together with an associated ''test suite'', using an ''incremental model learning'' which keeps under control the ''state space explosion''. In the following, we will refer to this process as the ''Learn DFCA'' algorithm. | ||
The state model constructed is based on the concept of ''deterministic finite cover automaton (DFCA)'' of a finite set <math>L</math>, which is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deterministic_finite-state_machine deterministic finite automaton] which accepts all sequences in <math>L</math> but may also accept sequences that are longer than every sequence in <math>L</math>, with respect to an upper bound <math>l</math> on the length of the considered sequences. | The state model constructed is based on the concept of ''deterministic finite cover automaton (DFCA)'' of a finite set <math>L</math>, which is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deterministic_finite-state_machine deterministic finite automaton] which accepts all sequences in <math>L</math> but may also accept sequences that are longer than every sequence in <math>L</math>, with respect to an upper bound <math>l</math> on the length of the considered sequences. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
The ''state model'' is constructed in a gradual manner, permitting the integration of the ''refinement'' in this process. | The ''state model'' is constructed in a gradual manner, permitting the integration of the ''refinement'' in this process. | ||
Whenever the generated ''cover automaton'' is found inaccurate, a ''counterexample path (a collection of events)'' must be | Whenever the generated ''cover automaton'' is found inaccurate, a ''counterexample path (a collection of events)'' must be provided and the ''Learn DFCA'' algorithm must be executed. | ||
=== Starting the plugin === | === Starting the plugin === | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
====Setting the constant value==== | ====Setting the constant value==== | ||
The first step requires the user to specify the value for the ''maximum sequence length'' constant (<math>l</math>), which is the upper bound on the length of the event sequences accepted by the | The first step requires the user to specify the value for the ''maximum sequence length'' constant (<math>l</math>), which is the upper bound on the length of the event sequences accepted by the ''cover automaton'' which will be generated. | ||
[[Image:MBT_for_Event-B_Screenshot__-2.png]] | [[Image:MBT_for_Event-B_Screenshot__-2.png]] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
The second wizard page displays the computed ''cover automaton'' and eventually the ''timeout paths''. | The second wizard page displays the computed ''cover automaton'' and eventually the ''timeout paths''. | ||
In the graphical representation of the automaton, the final states are drawn in double line, whereas non-final states are drawn in single line. The initial state is labeled q0. | In the graphical representation of the automaton, the final states are drawn in double line, whereas non-final states are drawn in single line. The initial state is labeled q0 and the transitions are labeled with event names. | ||
A ''timeout path'' is a sequence of events of length at most | A ''timeout path'' is a sequence of events of length at most <math>l</math>, for which no ''test data'' were found to trigger it. | ||
[[Image:MBT_for_Event-B_Screenshot__-3.png]] | [[Image:MBT_for_Event-B_Screenshot__-3.png]] | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
* moving the generated automaton as a whole | * moving the generated automaton as a whole | ||
* repositioning selected states of the automaton or highlighting transitions | * repositioning selected states of the automaton or highlighting transitions | ||
* displaying the generated test suite | * displaying the generated ''test suite'' | ||
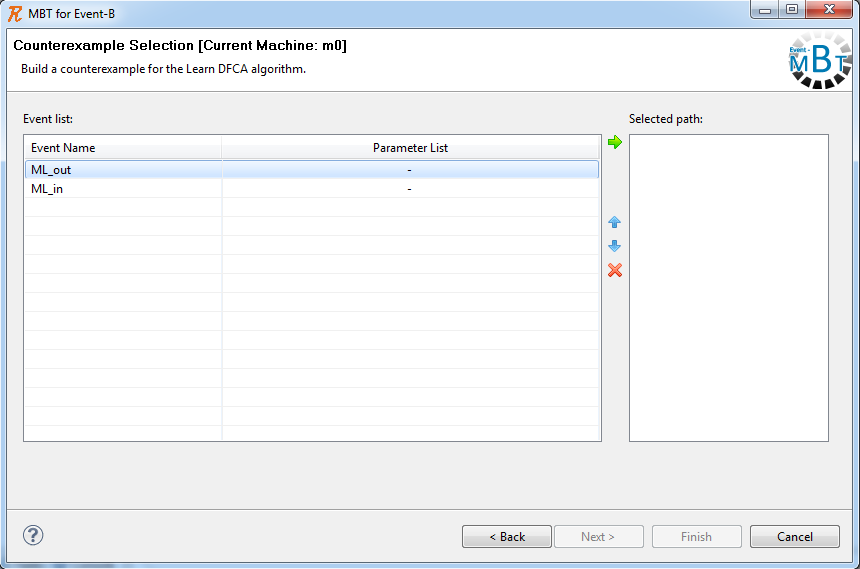
* providing a ''counterexample path'' | * providing a ''counterexample path'' | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
By choosing to view the generated ''test suite'' a list of ''test cases'' is provided, along with the corresponding ''test data''. | By choosing to view the generated ''test suite'' a list of ''test cases'' is provided, along with the corresponding ''test data''. | ||
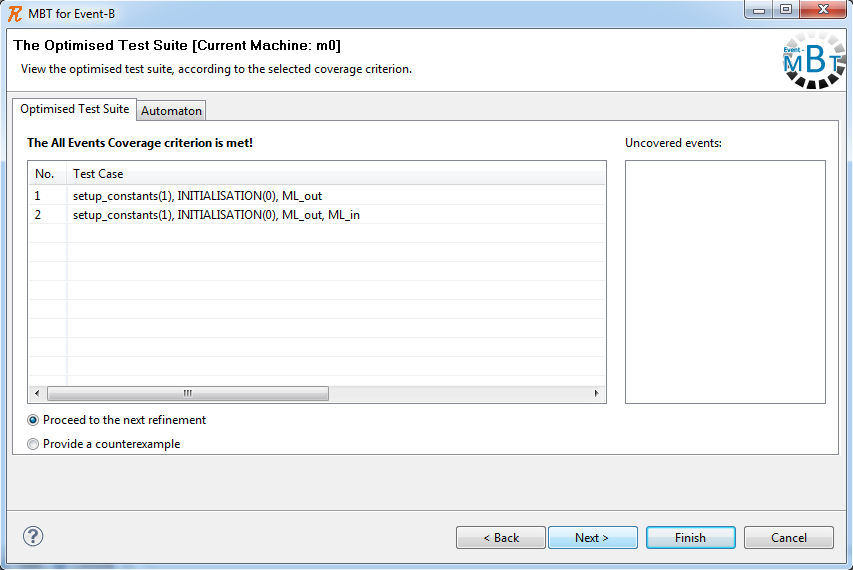
The MBT for Event-B plugin provides a means for optimizing a ''test suite'' according to a chosen ''coverage criteria'', | The MBT for Event-B plugin provides a means for optimizing a ''test suite'' according to a chosen ''coverage criteria'', e.g. ''all events coverage criterion''. | ||
[[Image:MBT_for_Event-B_Screenshot__-4.png]] | [[Image:MBT_for_Event-B_Screenshot__-4.png]] | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
Based on the user selection, the following options are available: | Based on the user selection, the following options are available: | ||
* proceed to the next ''refinement'', causing the Learn DFCA algorithm to be executed for a more concrete machine which refines the current one | * proceed to the next ''refinement'', causing the ''Learn DFCA'' algorithm to be executed for a more concrete machine which refines the current one | ||
* providing a counterexample path | * providing a '''counterexample path'' | ||
Revision as of 18:04, 7 July 2011
MBT (Model-Based Testing) for Event-B plugin
Installing
The MBT for Event-B plugin (also referred to as MBT plugin) relies on Rodin release 2.0 or newer and ProB plugin 2.2 or newer. The following steps will guide you through the installation process:
- Download the latest Rodin release for your platform from Sourceforge.
- Extract the downloaded zip file.
- Start Rodin from the folder where you extracted the zip file in the previous step.
- Install the ProB plugin:
- See ProB instalation instructions...
- Install the MBT plugin:
- In the menu choose Help -> Install New Software....
- Click Add....
- As Location enter http://fmi.upit.ro/mbt_plugin
- Enter a name e.g. MBT for Event-B Plugin.
- Click Ok.
- In the menu choose Help -> Install New Software....
- Restart Rodin as suggested.
Now you should be ready to use the MBT for Event-B plugin.
Usage
This section should help you to get started with the MBT plugin.
Short theoretical aspects
The MBT for Event-B plugin iteratively constructs a subset of the state space of an Event-B model (which is essentially an abstract state machine where the states can be implicitly derived from the values of the model variables), together with an associated test suite, using an incremental model learning which keeps under control the state space explosion. In the following, we will refer to this process as the Learn DFCA algorithm.
The state model constructed is based on the concept of deterministic finite cover automaton (DFCA) of a finite set 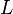 , which is a deterministic finite automaton which accepts all sequences in
, which is a deterministic finite automaton which accepts all sequences in 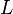 but may also accept sequences that are longer than every sequence in
but may also accept sequences that are longer than every sequence in 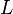 , with respect to an upper bound
, with respect to an upper bound 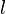 on the length of the considered sequences.
on the length of the considered sequences.
Given an Event-B model and an upper bound 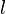 , the MBT plugin will incrementally construct finite cover automata that will eventually cover all executable event sequences of length less than or equal to
, the MBT plugin will incrementally construct finite cover automata that will eventually cover all executable event sequences of length less than or equal to 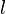 . Also, a set of test cases associated with the cover automata is evolved during iterations, along with the corresponding test data that makes them executable on the Event-B model.
. Also, a set of test cases associated with the cover automata is evolved during iterations, along with the corresponding test data that makes them executable on the Event-B model.
The execution of a test case implies the existence of appropriate test data for the events, i.e. appropriate values for the event parameters in order to ensure that the corresponding guard is true. By definition, test suite is a collection of test cases.
The state model is constructed in a gradual manner, permitting the integration of the refinement in this process.
Whenever the generated cover automaton is found inaccurate, a counterexample path (a collection of events) must be provided and the Learn DFCA algorithm must be executed.
Starting the plugin
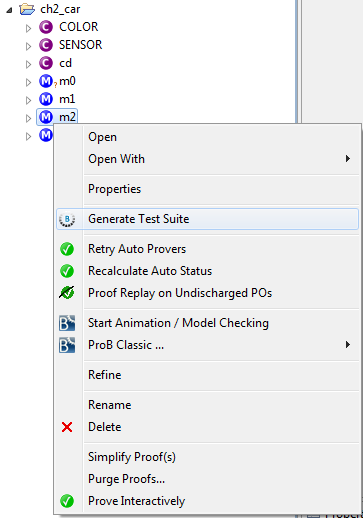
To start the MBT for Event-B plugin, the "Generate Test Suite" action must be selected from the context menu of an Event-B machine.
The plugin workflow is based on the concept of wizard, guiding the user step by step toward test suite generation.
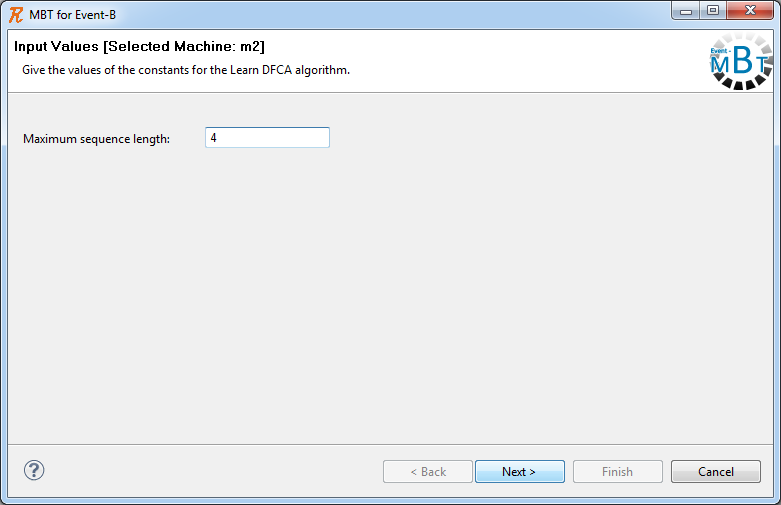
Setting the constant value
The first step requires the user to specify the value for the maximum sequence length constant (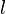 ), which is the upper bound on the length of the event sequences accepted by the cover automaton which will be generated.
), which is the upper bound on the length of the event sequences accepted by the cover automaton which will be generated.
By clicking the Next button, the Learn DFCA algorithm is executed, computing the deterministic finite cover automaton and the associated test suite along with the corresponding test data.
The generated cover automaton
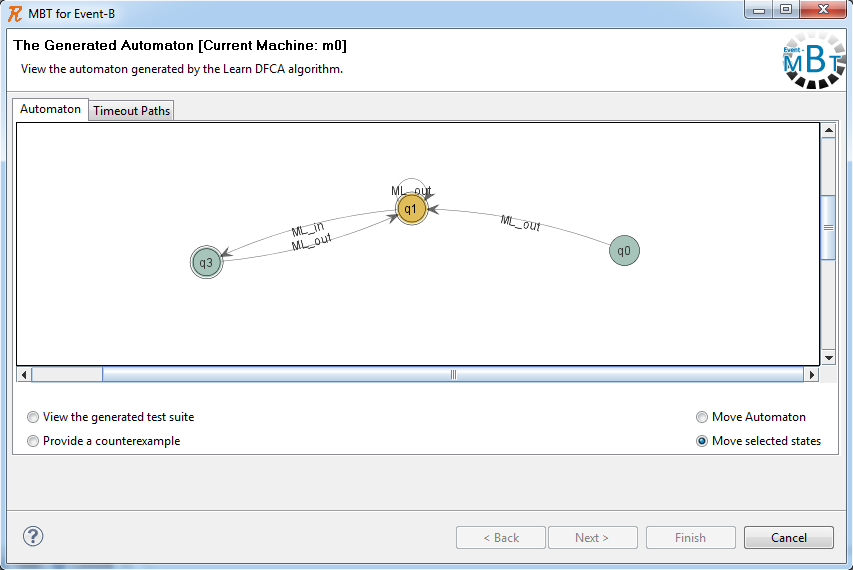
The second wizard page displays the computed cover automaton and eventually the timeout paths.
In the graphical representation of the automaton, the final states are drawn in double line, whereas non-final states are drawn in single line. The initial state is labeled q0 and the transitions are labeled with event names.
A timeout path is a sequence of events of length at most 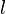 , for which no test data were found to trigger it.
, for which no test data were found to trigger it.
Based on the user selection, the following options are available:
- moving the generated automaton as a whole
- repositioning selected states of the automaton or highlighting transitions
- displaying the generated test suite
- providing a counterexample path
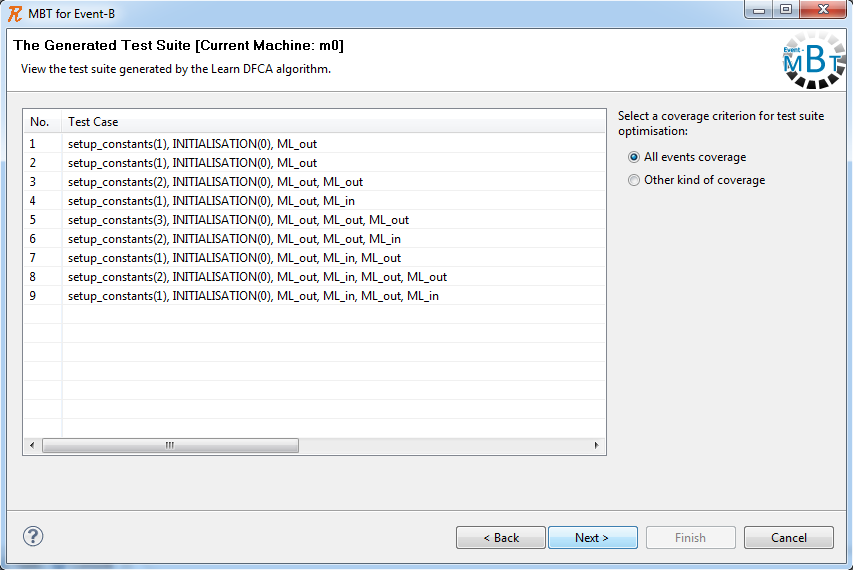
Display the generated test suite
By choosing to view the generated test suite a list of test cases is provided, along with the corresponding test data.
The MBT for Event-B plugin provides a means for optimizing a test suite according to a chosen coverage criteria, e.g. all events coverage criterion.
By selecting a coverage criterion and clicking Next the optimized test suite is displayed.
Display the optimized test suite
Based on the user selection, the following options are available:
- proceed to the next refinement, causing the Learn DFCA algorithm to be executed for a more concrete machine which refines the current one
- providing a 'counterexample path