Adding Manual Inference Reasoners: Difference between revisions
From Event-B
Jump to navigationJump to search
imported>Son New page: Beside the input sequent, reasoners of this type have two extra inputs specify the hypothesis or the goal and the position inside the predicate when apply an inference rule to the input s... |
imported>Son |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
* We will use Tom to implement the reasoner class itself. | * We will use Tom to implement the reasoner class itself. | ||
== Implement the Reasoner == | |||
The following steps is for implementing the reasoner using Tom. | |||
* Create a package within the ''src'' folder of the project with the name ''org.eventb.internal.contributors.seqprover.implinference''. | |||
* Create a Tom file within the newly created package with the name ''AutoInference.t''. | |||
* The content of the Tom file looks like this. | |||
package org.eventb.internal.contributors.seqprover.implinference; | |||
import java.math.BigInteger; | |||
import java.util.ArrayList; | |||
import java.util.Collection; | |||
import java.util.List; | |||
import java.util.Set; | |||
import java.util.HashSet; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.AssociativeExpression; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.AssociativePredicate; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.AtomicExpression; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.BinaryExpression; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.BinaryPredicate; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.BoolExpression; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.BoundIdentDecl; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.BoundIdentifier; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.DefaultFilter; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.Expression; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.Formula; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.FormulaFactory; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.FreeIdentifier; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.Identifier; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.IntegerLiteral; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.IPosition; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.LiteralPredicate; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.PowerSetType; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.Predicate; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.ProductType; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.QuantifiedExpression; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.QuantifiedPredicate; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.RelationalPredicate; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.SetExtension; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.SimplePredicate; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.Type; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.UnaryExpression; | |||
import org.eventb.core.ast.UnaryPredicate; | |||
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.eventbExtensions.Tactics; | |||
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.IProverSequent; | |||
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.IHypAction; | |||
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.ProverFactory; | |||
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.SequentProver; | |||
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.IProofRule.IAntecedent; | |||
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.eventbExtensions.Lib; | |||
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.eventbExtensions.Tactics; | |||
import org.eventb.internal.core.seqprover.eventbExtensions.AbstractManualInference; | |||
/** | |||
* Basic implementation for "manual implication inference" | |||
*/ | |||
@SuppressWarnings("unused") | |||
public class ManualInference extends AbstractManualInference { | |||
%include {Formula.tom} | |||
public String getReasonerID() { | |||
return "org.eventb.contributors.seqprover.implinference.manualInference"; | |||
} | |||
@Override | |||
protected String getDisplayName() { | |||
return "Manual deduction"; | |||
} | |||
@Override | |||
protected IAntecedent[] getAntecedents(IProverSequent seq, Predicate pred, | |||
IPosition position) { | |||
if (pred != null) | |||
return null; // This must be applied to goal | |||
if (position != IPosition.ROOT) | |||
return null; // The applicable position must be ROOT (the implication). | |||
Predicate goal = seq.goal(); | |||
Predicate P = null; | |||
Predicate Q = null; | |||
%match (Predicate goal) { | |||
/** | |||
* Deduction: | |||
* H, P |- Q | |||
* ----------- | |||
* H |- P => Q | |||
*/ | |||
Limp(PP, QQ) -> { | |||
P = `PP; | |||
Q = `QQ; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
if (P == null) | |||
return null; | |||
// There will be 1 antecidents | |||
IAntecedent[] antecidents = new IAntecedent[1]; | |||
// Added hypothesis P | |||
Set<Predicate> addedHyps = new HashSet<Predicate>(1); | |||
addedHyps.add(P); | |||
// Select the new hypothesis P | |||
IHypAction hypAction = ProverFactory.makeSelectHypAction(addedHyps); | |||
antecidents[0] = ProverFactory.makeAntecedent(Q, addedHyps, hypAction); | |||
return antecidents; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
Revision as of 13:00, 16 September 2008
Beside the input sequent, reasoners of this type have two extra inputs specify the hypothesis or the goal and the position inside the predicate when apply an inference rule to the input sequent. As an example, consider the following inference rule (called IMP_R).
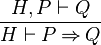
|
IMP_R |
In this simple case the location is the location of the implication symbol in the goal.
Declare the Reasoner
- Create a new plug-in project, e.g. org.eventb.contributors.seqprover.implinference. Deselect the plug-in options for "Generating an activator" and "Contribution to the UI".
- Add dependency on the project org.eventb.core.seqprover
- Add an extension for org.eventb.core.seqprover.reasoners for our implication rewrite reasoner, e.g.
<extension point="org.eventb.core.seqprover.reasoners">
<reasoner
class="org.eventb.internal.contributors.seqprover.implinference.ManualInference"
id="manualInference"
name="%manualInferenceName"/>
</extension>
(add the key manualInferenceName to the plugin.properties accordingly).
- We will use Tom to implement the reasoner class itself.
Implement the Reasoner
The following steps is for implementing the reasoner using Tom.
- Create a package within the src folder of the project with the name org.eventb.internal.contributors.seqprover.implinference.
- Create a Tom file within the newly created package with the name AutoInference.t.
- The content of the Tom file looks like this.
package org.eventb.internal.contributors.seqprover.implinference;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import org.eventb.core.ast.AssociativeExpression;
import org.eventb.core.ast.AssociativePredicate;
import org.eventb.core.ast.AtomicExpression;
import org.eventb.core.ast.BinaryExpression;
import org.eventb.core.ast.BinaryPredicate;
import org.eventb.core.ast.BoolExpression;
import org.eventb.core.ast.BoundIdentDecl;
import org.eventb.core.ast.BoundIdentifier;
import org.eventb.core.ast.DefaultFilter;
import org.eventb.core.ast.Expression;
import org.eventb.core.ast.Formula;
import org.eventb.core.ast.FormulaFactory;
import org.eventb.core.ast.FreeIdentifier;
import org.eventb.core.ast.Identifier;
import org.eventb.core.ast.IntegerLiteral;
import org.eventb.core.ast.IPosition;
import org.eventb.core.ast.LiteralPredicate;
import org.eventb.core.ast.PowerSetType;
import org.eventb.core.ast.Predicate;
import org.eventb.core.ast.ProductType;
import org.eventb.core.ast.QuantifiedExpression;
import org.eventb.core.ast.QuantifiedPredicate;
import org.eventb.core.ast.RelationalPredicate;
import org.eventb.core.ast.SetExtension;
import org.eventb.core.ast.SimplePredicate;
import org.eventb.core.ast.Type;
import org.eventb.core.ast.UnaryExpression;
import org.eventb.core.ast.UnaryPredicate;
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.eventbExtensions.Tactics;
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.IProverSequent;
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.IHypAction;
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.ProverFactory;
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.SequentProver;
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.IProofRule.IAntecedent;
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.eventbExtensions.Lib;
import org.eventb.core.seqprover.eventbExtensions.Tactics;
import org.eventb.internal.core.seqprover.eventbExtensions.AbstractManualInference;
/**
* Basic implementation for "manual implication inference"
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class ManualInference extends AbstractManualInference {
%include {Formula.tom}
public String getReasonerID() {
return "org.eventb.contributors.seqprover.implinference.manualInference";
}
@Override
protected String getDisplayName() {
return "Manual deduction";
}
@Override
protected IAntecedent[] getAntecedents(IProverSequent seq, Predicate pred,
IPosition position) {
if (pred != null)
return null; // This must be applied to goal
if (position != IPosition.ROOT)
return null; // The applicable position must be ROOT (the implication).
Predicate goal = seq.goal();
Predicate P = null;
Predicate Q = null;
%match (Predicate goal) {
/**
* Deduction:
* H, P |- Q
* -----------
* H |- P => Q
*/
Limp(PP, QQ) -> {
P = `PP;
Q = `QQ;
}
}
if (P == null)
return null;
// There will be 1 antecidents
IAntecedent[] antecidents = new IAntecedent[1];
// Added hypothesis P
Set<Predicate> addedHyps = new HashSet<Predicate>(1);
addedHyps.add(P);
// Select the new hypothesis P
IHypAction hypAction = ProverFactory.makeSelectHypAction(addedHyps);
antecidents[0] = ProverFactory.makeAntecedent(Q, addedHyps, hypAction);
return antecidents;
}
}