Structured Types: Difference between revisions
imported>WikiSysop |
imported>WikiSysop |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
''E'' and ''F'' can be any type definable in Event-B, including a type representing a record structure. | ''E'' and ''F'' can be any type definable in Event-B, including a type representing a record structure. | ||
==Constructing Structured Values== | |||
==Extending Structured Types== | |||
==Recursive Structured Types== | |||
==Structured Variables== | |||
Revision as of 16:11, 1 May 2009
Modelling Structured Types
The Event-B mathematical language currently does not support a syntax for the direct definition of structured types such as records or class structures. Nevertheless it is possible to model structured types using projection functions to represent the fields/attributes. For example, suppose we wish to model a record structure C with fields e and f (with type E and F respectively). Let us use the following syntax for this (not part of Event-B syntax):
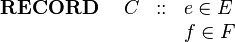
|
We can model this structure in Event-B by introducing (in a context) a carrier set C and two functions e and f as constants as follows:
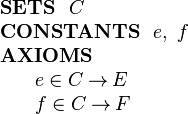
|
Now, given an element 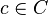 representing a record structure, we write
representing a record structure, we write 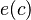 for the e component of c and
for the e component of c and 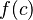 for the f component of c.
for the f component of c.
E and F can be any type definable in Event-B, including a type representing a record structure.