Extending the Static Checker
Introduction
The purpose of this page is to describe how to extend the static checker. It covers on the one hand, the definition of the extension, and on the other hand its implementation.
The useful extension points are listed below; they offer the possibility to contribute to the static checker:
- org.rodinp.core.autoTools
- org.eventb.core.configurations
- org.rodinp.core.internalElementTypes
- org.eventb.core.scModuleTypes
- org.eventb.core.scStateTypes
Before Starting
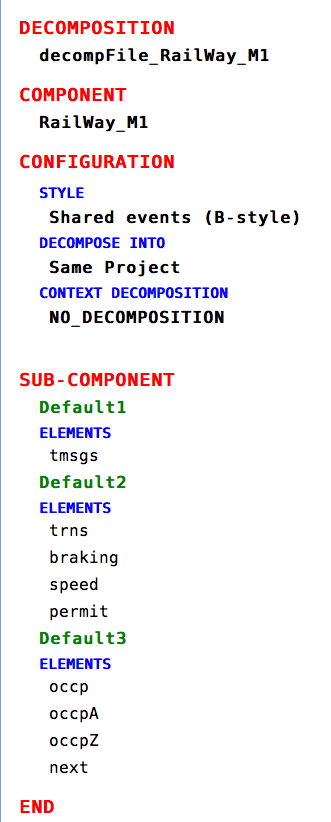
It is necessary to define the static checked elements that are similar to the unchecked elements. We will use as an example the decompositionFile that is defined as follows:
- decompositionFile
- decompositionRoot
- Component (machine to be decomposed)
- Configuration (style: shared events/shared variables;newProjectOption: decompose in the same project/different projects;decomposeContextOption:no decomposition/minimal decomposition)
- SubComponent (resulting decomposed parts)
- SubComponentElement (elements used to decompose: variables for shared event decomposition and events for shared variable decomposition)
- decompositionRoot
To extend the static checker, it is necessary to add a new content type (org.eclipse.core.contenttype.contentTypes) containing the checked version of the decompositionFile:
<content-type
base-type="org.rodinp.core.rodin"
file-extensions="dcc,dcc_tmp"
id="scDcpFile"
name="Event-B Statically Checked Decomposition File"
priority="normal">
</content-type>
and the respective file association (org.rodinp.core.fileAssociations):
<fileAssociation
content-type-id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.scDcpFile"
root-element-type="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.scDcpFile">
</fileAssociation>
The respective static checked elements must be added as internal elements using the extension org.rodinp.core.internalElementTypes:
<extension
point="org.rodinp.core.internalElementTypes">
<internalElementType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.basis.DecompositionRoot"
id="dcpFile"
name="%eventBdcpFile">
</internalElementType>
<internalElementType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.basis.SCDecompositionRoot"
id="scDcpFile"
name="Event-B Statically Checked Decomposition Root">
</internalElementType>
<internalElementType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.basis.DecompositionConfiguration"
id="configuration"
name="%eventBDecompositionConfiguration">
</internalElementType>
<internalElementType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.basis.SCDecompositionConfiguration"
id="scConfiguration"
name="Event-B Statically Checked Decomposition Configuration">
</internalElementType>
</extension>
In the above example, the first internal element type is the unckecked internal element, and the second is the same internal element but in the checked version. Having the checked elements defined, we can start to extend the static checker for our files and respective elements.
AutoTools
The static checker it is a tool that runs automatically. In order to implement the tool, it is necessary to define the following extension point org.rodinp.core.autoTools. This extension point allows tools to run automatically when changes to the Rodin database are committed. To implement the reactive model of Rodin, automatic tools run only when one of their input files has changed. As such, for each automatic tool, plugin developers must provide two kinds of contributions:
- Some dependency extractors.
- The tool itself.
Declaration
The autoTools extension-point allows tool writers to register their tool implementation under a symbolic name that is then used by the Rodin platform to find and run the tool. The symbolic name is the id of the tool extension. An example of the implementation of a static checker can be seen as follows:
<extension
point="org.rodinp.core.autoTools">
<tool
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.internal.core.sc.DecompositionStaticChecker"
id="decompositionSC"
name="Decomposition Static Checker">
<extractor
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.internal.core.sc.DecompositionStaticChecker"
name="Decomposition Extractor of Static Checker">
<inputType
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.dcpFile">
</inputType>
</extractor>
</tool>
</extension>
We defined a static checker tool that will run for the defined input type (ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.dcpFile). The class provided for extractors shall implement the org.rodinp.core.builder.IExtractor interface, while the class provided for tools themselves shall implement org.rodinp.core.builder.IAutomaticTool.
The Rodin platform (see plug-in org.eventb.core) provides a static checking automatic tool for context/machine files.
Programmatic usage
The class to be implemented usually extends the class org.eventb.core.sc.StaticChecker and needs to implement the abstract method extract from the interface org.rodinp.core.builder.IExtractor:
public void extract(IFile file, IGraph graph, IProgressMonitor monitor)throws CoreException {
try {
monitor.beginTask(Messages.bind(Messages.build_extracting, file.getName()), 1);
IRodinFile source = RodinCore.valueOf(file);
IDecompositionRoot root = (IDecompositionRoot) source.getRoot();
IRodinFile target = root.getSCDecompositionRoot().getRodinFile();
graph.addTarget(target.getResource());
graph.addToolDependency(source.getResource(), target.getResource(),true);
} finally {
monitor.done();
}
}
The interface org.rodinp.core.builder.IGraph is used by the extractors registered with the builder to manipulate the dependency graph of all Rodin resources of a Rodin project. It is a façade to the more complicated ways of manipulating the dependency graph inside the builder. Some information is cached in the corresponding object, so the contents of the façade must be synchronised with the graph at the end of an extraction. Requests to add nodes to the graph must be made explicitly by calls to the method addNode. Dependencies are managed by the façade. It saves clients to have to compute dependency graph deltas themselves.
We have already defined the static checking tool and the target for which it will run. Now, we need to configure the static checker tool. It is necessary to define the checks that are required for each element and this is done by providing an extension to org.eventb.core.configurations.
Configuration
Configuration is used to define which modules are used by the static checker tool. Similarly in can be used for the proof obligation generator (POG).
Declaration
<!ELEMENT configuration ((config | pogModule | scModule))+> <!ATTLIST configuration id CDATA #REQUIRED name CDATA #REQUIRED > id - the identifier for this attribute type (simple id token, unique for attribute types within the extension namespace). The token cannot contain dot (.) or whitespace. name - the human-readable name of this attribute type
For static checks, we use scModule and config elements. Below we show an example of using the configuration:
<extension
point="org.eventb.core.configurations">
<configuration
id="dcmpSC"
name="Decomposition Static Checker Root Module">
<scModule
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.decompositionModule">
</scModule>
</configuration>
<configuration
id="dcmpBaseSC"
name="Decomposition Static Checker Base Module">
<config
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.dcmpSC">
</config>
<scModule
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.componentModule">
</scModule>
<scModule
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.decompositionConfigurationModule">
</scModule>
<scModule
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.subComponentModule">
</scModule>
<scModule
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.subComponentElementModule">
</scModule>
</configuration>
<configuration
id="dcmp"
name="Decomposition Configuration">
<config
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.dcmpBaseSC">
</config>
</configuration>
</extension>
Although not necessary, we structure the configuration in different levels:
- The ‘Decomposition Configuration’ is defined by a base static checker module that contains the ‘Decomposition Static Checker Base Module‘.
- Inside the last one are the static check modules for all elements (decompositionComponentModule,decompositionConfigurationModule,...) in the decompositionFile including decompositionRoot (id=dcmpSC).
The id field in the scModule tags must exist already. They will correspond to the static checker modules defined using the extension ‘org.eventb.core.scModuleTypes‘. These are used to process the necessary operations for each element inside a static checked file.
Programmatic usage
Modules
Filter
Filter are used to validate inserted elements. After the successful validation of all elements, they can be processed and stored in the static checked file. In order to implement a filter, we define the following extension-point:
<!ELEMENT filterType (prereq)*> <!ATTLIST filterType id CDATA #REQUIRED name CDATA #REQUIRED parent CDATA #REQUIRED class CDATA #REQUIRED > id - the identifier for this filter type (simple id token, unique for (filter/processor/root) types within the extension namespace). The token cannot contain dot (.) or whitespace. name - the human-readable name of this filter module parent - the optional parent (processor) module. Root modules must leave the attribute undefined. It is not allowed to choose a filter module as parent. class - the fully-qualified name of a subclass of org.eventb.core.sc.SCFilterModule
For the filterType, the classes usually extend the abstract class org.eventb.core.sc.SCFilterModule. It also contains three methods:
- public abstract boolean accept(IRodinElement element, ISCStateRepository repository, IProgressMonitor monitor) throws CoreException;: runs the static checker module. Returns whether the element should be accepted. If an error marker was associated with the element the returned value should usually be false. Exceptions from this rule are possible, in particular, if the element has been already marked with an error.
- public abstract void initModule(ISCStateRepository repository,IProgressMonitor monitor) throws CoreException;:Initialisation code for the module
- public abstract void endModule(ISCStateRepository repository,IProgressMonitor monitor) throws CoreException;: Termination code for the module
Processor
Processor literally process the elements, storing them in the static checked file, running sub-processors and adding states to the repository if required. To implement a processor, it is required to define the following extension-point:
<!ELEMENT processorType (prereq)*> <!ATTLIST processorType id CDATA #REQUIRED name CDATA #REQUIRED parent CDATA #REQUIRED class CDATA #REQUIRED > id - the identifier for this processor type (simple id token, unique for (filter/processor/root) types within the extension namespace). The token cannot contain dot (.) or whitespace. name - the human-readable name of this processor module parent - the optional parent (processor) module. Root modules must leave the attribute undefined. It is not allowed to choose a filter module as parent. class - the fully-qualified name of a subclass of org.eventb.core.sc.SCProcessorModule
The classes that implement the rootType and processorType usually extend the abstract class org.eventb.core.sc.SCProcessorModule. They contain a constant called MODULE_TYPE that identifies the scModule. An example is:
public static final IModuleType<DecompositionModule> MODULE_TYPE = SCCore.getModuleType(DecompositionCorePlugin.PLUGIN_ID + ".decompositionModule");
that identifies the Decomposition Root Module. Moreover this classes should implement the three methods that are part of the interface org.eventb.internal.core.tool.types.ISCProcessorModule:
- public abstract void initModule(IRodinElement element,ISCStateRepository repository,IProgressMonitor monitor) throws CoreException; : Initialisation code for the module. Used to initialise the global variables of the class.
- public abstract void process(IRodinElement element,IInternalElement target, ISCStateRepository repository, IProgressMonitor monitor) throws CoreException;: Runs the static checker module: process the element. The element itself has already been accepted. If this element has children, then the children modules should be called here (see for example ‘ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.modules.DecompositionSubComponentModule‘).
- public abstract void endModule(IRodinElement element,ISCStateRepository repository,IProgressMonitor monitor) throws CoreException; : Termination code for the module. Used to clean up memory (global variables) before finishing the module call.
Sequencing
Parent
Similar to processor by applied to the root of the file. The extension that need to be implemented in defined below:
<!ELEMENT rootType EMPTY> <!ATTLIST rootType id CDATA #REQUIRED name CDATA #REQUIRED input CDATA #REQUIRED class CDATA #REQUIRED > id - the identifier for this root type (simple id token, unique for (filter/processor/root) types within the extension namespace). The token cannot contain dot (.) or whitespace. name - the human-readable name of this root module input - identifier of the input file element type for this root module. class - the fully-qualified name of a subclass of org.eventb.core.sc.SCProcessorModule
Prerequisite
Some static checks rely on already done static checks so they work as pre-requirements. For instance, if a concrete event is refined it is necessary to know the abstract machine defined in the refine machine section. So the refine machine is a static check pre-requirement of the refinement an event. To implement a pre-requirement, it is necessary to define the following extension-point:
<!ELEMENT prereq EMPTY> <!ATTLIST prereq id CDATA #REQUIRED > id - the full ids of all (filter and processor) modules that must be run before this module
Example
An example of defining a scModule of type rootType, filterType and pre-requirement is defined below:
<extension
point="org.eventb.core.scModuleTypes">
<rootType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.modules.DecompositionModule"
id="decompositionModule"
input="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.dcpFile"
name="Decomposition SC Root Module">
</rootType>
<processorType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.modules.DecompositionComponentModule"
id="decompositionComponentModule"
name="Decomposition SC Component Module"
parent="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.decompositionModule">
</processorType>
.
.
.
<filterType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.modules.DecompositionSubComponentElementFilterModule"
id="decompositionSubComponentElementFilterModule"
name="Decomposition SC SubComponentElement Filter Module"
parent="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.decompositionCommitSubComponentElementModule">
<prereq
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.decompositionConfigurationModule">
</prereq>
<prereq
id="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.decompositionComponentModule">
</prereq>
</filterType>
</extension>
Below is an example of the call of the three processor/root methods in the class ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.modules.DecompositionModule:
@Override
public void initModule(IRodinElement element,ISCStateRepository repository, IProgressMonitor monitor) throws CoreException {
accuracyInfo = new DecompositionAccuracyInfo();
final IDecompositionLabelSymbolTable labelSymbolTable = new DecompositionLabelSymbolTable(LABEL_SYMTAB_SIZE);
repository.setState(labelSymbolTable);
repository.setState(accuracyInfo);
initProcessorModules(element, repository, monitor);
}
public void process(IRodinElement element, IInternalElement target,ISCStateRepository repository, IProgressMonitor monitor)throws CoreException {
scRoot = (ISCDecompositionRoot) target;
processModules(element, target, repository, monitor);
}
@Override
public void endModule(IRodinElement element,ISCStateRepository repository, IProgressMonitor monitor) throws CoreException {
scRoot.setAccuracy(accuracyInfo.isAccurate(), monitor);
endProcessorModules(element, repository, monitor);
}
Whenever a problem is encountered by the static checker, it is possible to raise a warning or an error, highlighting the respective element using the method org.eventb.core.sc.SCModule#createProblemMarker. An example can be seen below:
public void process(IRodinElement element, IInternalElement target,ISCStateRepository repository, IProgressMonitor monitor)throws CoreException {
monitor.subTask(Messages.bind(Messages.progress_DecompositionComponent));
IComponent[] decompositionComponents = decompositionFile.getDecompositionComponents();
if (decompositionComponents.length > 1) {
for (int k = 1; k < decompositionComponents.length; k++) {
createProblemMarker(decompositionComponents[k], DecompositionConfigurationAttributes.TARGET_ATTRIBUTE,
DecompositionGraphProblem.TooManyComponentsError);
}
}
...
repository.setState(new ComponentMachineInfo(scComponentMachineRoot,component));
...
monitor.worked(1);
}
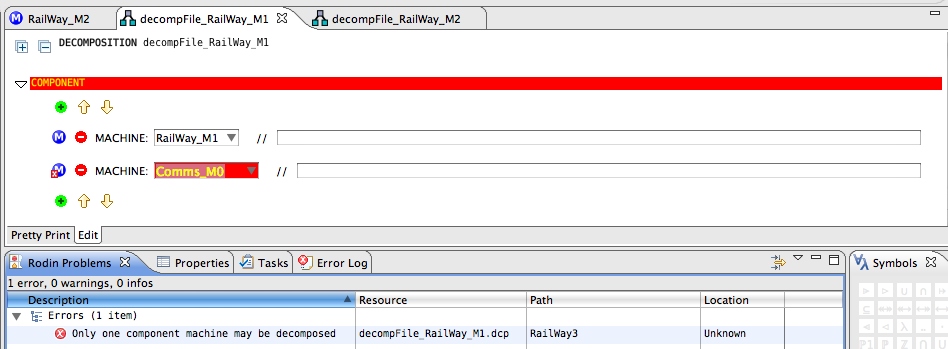
In this particular case, if the number of IComponent elements is >1, then an error will be generated for the respective IComponent element:
States
The static check of the elements in a file are independent of each other (different and independent modules). Nevertheless there are some information that is dependent on other elements. For instance, for label elements it is necessary to know which labels have been used already before checking the elements. Since the elements checks are independent, the solution is to ‘share data‘ through scStates implemented using the extension-point org.eventb.core.scStateTypes. These are used to dynamically store data that will be used by dependencies (scModules) inside the static checked elements. The data is stored in a SCStateRepository and contains a key and respective content (value).
Declaration
<!ELEMENT stateType EMPTY> <!ATTLIST stateType id CDATA #REQUIRED name CDATA #REQUIRED class CDATA #REQUIRED > id - the identifier for this attribute type (simple id token, unique for attribute types within the extension namespace). The token cannot contain dot (.) or whitespace. name - the human-readable name of this attribute type class - the fully-qualified name of a subclass of org.eventb.core.sc.state.ISCState
Programatic Usage
To store data, we need to call the method
void setState(I state) [I extends IState]
part of the interface org.eventb.core.tool.IStateRepository (See method initModule above). To retrieve a state, you call the method:
I getState(IStateType<? extends I> stateType) throws CoreException;
In order to use the state, it is necessary to define the ‘key‘ in the extension point stateType.
Example
An example of the use of states can be seen below:
<extension
point="org.eventb.core.scStateTypes">
<stateType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.state.IDecompositionAccuracyInfo"
id="decompositionAccuracyInfo"
name="Decomposition Accuracy Info">
</stateType>
<stateType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.state.IDecompositionLabelSymbolTable"
id="decompositionLabelSymbolTable"
name="Decomposition Label-Symbol Table">
</stateType>
<stateType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.state.IComponentAccuracyInfo"
id="componentDecompositionInfo"
name="Decomposition Component Machine Information">
</stateType>
<stateType
class="ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.core.sc.state.IDecompositionStyle"
id="style"
name="Decomposition Style">
</stateType>
</extension>
For instance, the last stateType defined above is Decomposition Style. It is required for checking which kind of subComponentElements are expected:
- if style= shared event => subComponentElement type must be variables.
- if style= shared variable => subComponentElement type must be events.