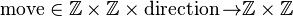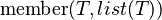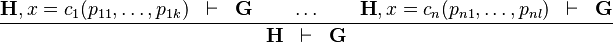Datatype Rules
From Event-B
Datatype rules may seem a bit difficult to understand at first sight. Here are a few examples intended to make them clearer.
Datatypes used
The rules will be applied to the following datatypes:
Directions:
direction ::=
north
| east
| south
| west
Let us have a function
first two arguments are a start position, third is a direction, result is the end position.
Lists:
list(T) ::=
nil
| cons( head : T, tail : list(T) )
Let us have a predicate
meaning that the first argument is a member of the list.
Trees:
tree(T) ::= empty | node( left : tree(T), value : T, right : tree(T) )
Let us have a function
defining the height of a tree
Distinct Case
The rule states
Application to directions
TODO
!x,y,dir . move(x,y,dir) /= x |-> y
Application to lists
TODO
!l oftype list(\Z). #x. member(x,l) & (!y. member(y,l) => y <= x)
evidence that nil list has been forgotten in the predicate
Application to trees
TODO
Induction
TODO