Decomposition Plug-in User Guide
Introduction
The Decomposition plug-in allows to decompose a model into sub-models.
See the Event-B Model Decomposition page for technical details on shared variables (A-style) decomposition.
Installing and Updating
Setup
The following steps will guide you through the setup process:
- Download Rodin for your platform from Sourceforge:
- Extract the downloaded zip file.
- Start Rodin from the folder where you extracted the zip file in the previous step.
- Install the Decomposition plug-in:
- In the menu choose Help -> Software Updates...
- Select the tab Available Software and click Add Site...
- Use the location URL: http://rodin-b-sharp.sourceforge.net/updates
- Back in Available Software open the update site you just added
- Select Event-B Decomposition and click Install...
- Restart Rodin as suggested.
Now you are ready to use the Decomposition plug-in.
Update
The following steps will guide you through the update process:
- In Rodin open the preferences (Window -> Preferences or for Mac: Rodin -> Preferences)
- Find Install/Update -> Automatic Updates
- Select Automatically find new updates and notify me
As soon as Rodin finds a new update it will ask you if you would like to install it.
Release Notes
See the Decomposition plug-in release history.
Decomposing
TODO
Selecting the Input Machine
Setting the Preferences
Decomposition style, decomposition of the contexts, etc.
Importing / Exporting the Configuration
Reporting a Bug or Requesting a Feature
Please, use the SourceForge trackers to report a bug on existing features, or to request new features:
Error Messages
When running the decomposition
The decomposition is forbidden, and an error message is displayed, if one of the following conditions applies:
- The built INITIALISATION events of the sub-machines would define an action modifying at the same time a private variable and a shared variable.
- Action {0} of the INITIALISATION event modifies a private variable and a shared variable
- See Ensuring that a shared variable is not refined by an initialization event for further explanations.
- The sub-models shall be created in new Event-B projects, but one of the entered project names already exists.
- The project {0} should not exist
- The same project name has been entered for two distinct sub-models.
- Duplicate sub-model names: {0}
When running the static checker
The following rules are enforced by the static checker, and errors are returned (in the Rodin Problems view) accordingly:
- A shared variable shall be present in subsequent refinements.
- Shared variable {0} has disappeared
- A shared variable shall still have the shared attribute in subsequent refinements.
- Inconsistent nature of shared variable {0}, shared expected
- An external event shall be present in subsequent refinements.
- External event {0} has disappeared
- An external event shall still have the external attribute in subsequent refinements.
- Inconsistent status of external event {0}, external expected
- An external event shall have the extended attribute in subsequent refinements.
- Inconsistent status of external event {0}, extended expected
- An external event shall not declare any additional parameter in subsequent refinements.
- Parameters cannot be added in external events
- An external event shall not declare any additional guard in subsequent refinements.
- Guards cannot be added in external events
- An external event shall not declare any additional action in subsequent refinements.
- Actions cannot be added in external events
- An INITIALISATION event shall not contain an action modifying at the same time a private variable and a shared variable.
- Action {0} of the INITIALISATION event modifies a private variable and a shared variable
- The actions of an INITIALISATION event modifying a shared variable shall be present and be syntactically equal in subsequent refinements.
- Action {0} of the INITIALISATION event has disappeared
For additional information, see:
- Ensuring that a shared variable is not refined.
- Ensuring that an external event is not refined.
- Ensuring that a shared variable is not refined by an initialization event.
Tips and Tricks
- An invariant is missing in a sub-machine, but I would like to have it copied.
- For example, an invariant between a concrete variable and some abstract variable may be useful.
- A solution is to add a theorem based on the missing predicate in the non-decomposed machine. See the last paragraph about the invariants in the Event-B Model Decomposition page.
- An axiom is missing in a sub-context, but I would like to have it copied.
- Such a situation may be encountered if the "Decompose contexts" option is checked.
- The workaround proposed for the invariants applies to the axioms as well.
- For example, if the non-decomposed context defines the axiom
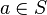 , and this axiom is not copied in a sub-context which contains the
, and this axiom is not copied in a sub-context which contains the 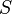 carrier set but does not contain the
carrier set but does not contain the 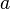 constant, then the information
constant, then the information 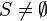 is lost. In order to keep it, it is possible to add the theorem
is lost. In order to keep it, it is possible to add the theorem 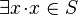 in the non-decomposed context.
in the non-decomposed context.
- A variable is tagged as private in a sub-machine, but I would like to have it tagged shared.
- Such a behavior is suitable if you want to prevent this variable from being further refined.
- A solution for such a variable
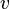 of a sub-machine
of a sub-machine  is to add a fake action
is to add a fake action 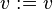 in a event of the non-decomposed machine which is associated to the sub-machine
in a event of the non-decomposed machine which is associated to the sub-machine 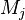 (
( and
and 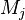 are distinct sub-machines) when performing the decomposition.
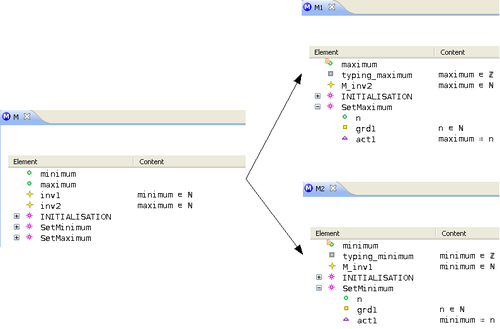
are distinct sub-machines) when performing the decomposition. - In the first example below, the
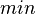 variable will become private when performing the decomposition:
variable will become private when performing the decomposition:
- In the second example below, the
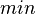 variable will become shared when performing the decomposition:
variable will become shared when performing the decomposition:
