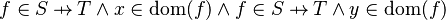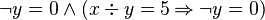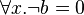Improved WD Lemma Generation
This page describes work in progress for optimising well-definedness lemmas generated by the Core Rodin platform.
The lemmas are generated according to the 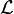 operator defined in Well-definedness in Event-B. However, this operator being defined as a syntactic transformation, it sometimes generates lemmas that are unnecessarily complicated. We first give some motivating examples showing cases where this happens, then we describe what result shall be produced by the tool. Finally, we describe the design retained for development.
operator defined in Well-definedness in Event-B. However, this operator being defined as a syntactic transformation, it sometimes generates lemmas that are unnecessarily complicated. We first give some motivating examples showing cases where this happens, then we describe what result shall be produced by the tool. Finally, we describe the design retained for development.
Motivating Examples
All examples corresponds to the behavior of Rodin 1.3
Example A
The well-definedness lemma generated for predicate 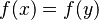 is
is
This predicate is sub-optimal as it contains twice the same sub-predicate (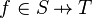 ). Consequently, when the prover is fed with the generated lemma, it will have to prove twice the same goal.
). Consequently, when the prover is fed with the generated lemma, it will have to prove twice the same goal.
Example B
The well-definedness lemma generated for predicate 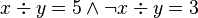 is
is
This predicate is sub-optimal as the sub-predicate 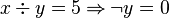 is subsumed by the sub-predicate
is subsumed by the sub-predicate 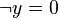 . The prover doesn't need to prove
. The prover doesn't need to prove 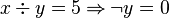 if
if 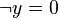 has been proved.
has been proved.
Example C
The well-definedness lemma generated for predicate 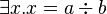 is
is
This predicate is sub-optimal as 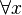 is unnecessary (
is unnecessary (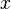 does not occur in the quantified predicate).
does not occur in the quantified predicate).
Improved Generation
To fix the issues shown in the above examples, we need that the tool produces a WD lemma equivalent (in the logical sense) to the predicate obtained through the 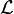 operator and satisfying the following constraints:
operator and satisfying the following constraints:
- No sub-predicate subsumes another sub-predicate.
- There is no unnecessary quantification.
TODO: Is there any other constraint to add?
Design for Improved Generation
TODO: Do the design