imported>Andy |
imported>Tommy |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | This page describes code generation approaches, and tools, developed at the University of Southampton between 2009 and 2015. It includes the Tasking Event-B approach; and also code generation for Functional Mock-up Units, for use with the Functional Mock-up Interface (FMI) standard. Tasking Event-B is an extension to Event-B, for defining concurrent systems sharing data, for details see the [[Tasking Event-B Overview]] page.
| + | {{Navigation|Previous= [[Introduction_(How_to_extend_Rodin_Tutorial)|Introduction]] | Up= [[Plug-in_Tutorial|How to extend Rodin Tutorial (Index)]] | Next= [[Extend_Rodin_database_(How_to_extend_Rodin_Tutorial)|Extend the database]]}} |
| | | | |
| − | Other code generation approaches that are available for Event-B include:
| + | === In this part === |
| − | * [http://poporo.uma.pt/favas/EventB2Java.html EventB2Java] generates JML-specified Java implementations of Event-B models. Contributions by Néstor Cataño, Tim Wahls, Camilo Rueda and Víctor Rivera. | + | * We will explain how to use Eclipse to easily create a plugin package structure for our implementation. Developers which are familiar with plugin building may skip this part and go to the next page of this tutorial. |
| − | * [http://poporo.uma.pt/favas/EventB2JML.html EventB2JML] translates Event-B machines to JML-specified Java abstract classes. Contributions by Néstor Cataño, Tim Wahls, Camilo Rueda and Víctor Rivera.
| + | Before starting to perform the following step, you should have your development environment ready and open. |
| − | * [http://poporo.uma.pt/eventb2dafny/Home.html EventB2Dafny] translates Event-B proof-obligations into the input language of Dafny. Developed by Néstor Cataño.
| |
| − | * [http://users.dickinson.edu/~wahlst/eventb2sql/eventb2sql.html EventB2SQL] translates Event-B machines to Java implementations that make the state of a machine persistent by storing it in a database.
| |
| − | * [http://eb2all.loria.fr/ EB2ALL] (Beta Version) supports automatic code generation from Event-B to C, C++, Java and C#.
| |
| − | * [[Code Generation|Tasking Event-B]] supports generation of multi-tasking Java, Ada, and OpenMP C code from Event-B.
| |
| − | * [[B2C plugin|B2C]] translates Event-B models to C source code, which may then be compiled using external C development tools.
| |
| − | * [http://www.eb2vhdl.tk/ EHDL] The plug-in enables [http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=6037401 VHDL code generation] from formal Event-B models automatically.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | === Step 1 === |
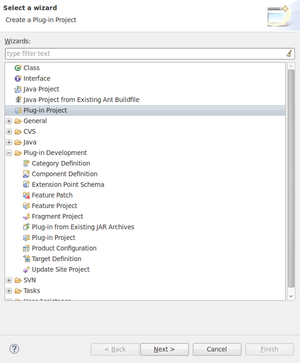
| | + | To create a plugin, go to "'''File > New > Other'''" and select "'''Plug-in Project'''" either from the general list if it appears, or from the category "Plug-in Development". |
| | + | Click on "'''Next'''". |
| | | | |
| | + | [[Image:Extend_Rodin_Tuto_1_1_File_new_plugin.png|300px]] |
| | | | |
| − | == Code Generation for Co-simulation using FMI - Rodin 2.8 == | + | === Step 2 === |
| − | 7th November 2014
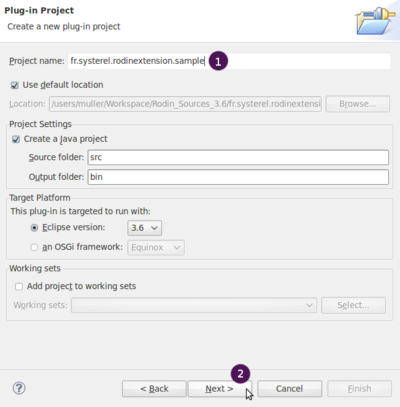
| + | The following wizard page appears: |
| | | | |
| − | For the ADVANCE project we have added the ability to generate C code from Event-B component diagrams. We target a particular style of C, which is tailored for use with ADVANCE's Functional Mock-up Interface ([http://eprints.soton.ac.uk/365249/1/rms.pdf FMI]) approach. To generate code, a component from a component diagram is selected. The code generator translates to C using a [http://eprints.soton.ac.uk/364265/1/Templates4CG.pdf template], and has a facility for packaging the code as a functional mock-up unit (FMU). The FMU can then be used in place of the Event-B component in the diagram for subsequent simulation. The generated C code can also be used to compile code to be used in the deployed product.
| + | [[Image:Extend_Rodin_Tuto_1_2_NewPlug-inProject.png|400px]] |
| | | | |
| − | The FMU C translation code must be built from the following sources:
| + | 1. In project name, enter the name of the plugin package that must appear in the project hierarchy. We used <tt>fr.systerel.rodinextension.sample</tt> but the formalism used often corresponds to <tt>mydomain.mycompany.mypluginname</tt> |
| | + | 2. Verify that the plugin is targeted to run with Eclipse 3.6 and click on "'''Next'''". |
| | | | |
| − | Code generation sources reside at:
| + | === Step 3 === |
| − | http://sourceforge.net/p/rodin-b-sharp/CodeGen/ci/master/tree/TaskingEventB/
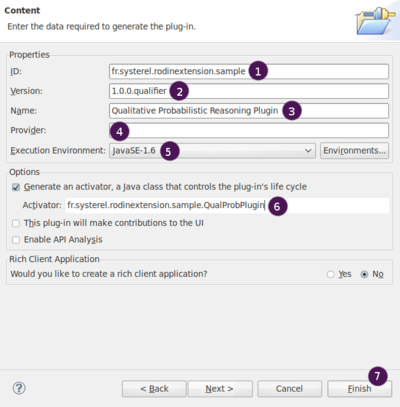
| + | [[Image:Extend_Rodin_Tuto_1_3_NewPlug-inProject_Content.png|400px]] |
| | | | |
| − | Sources specifically for generating the FMU C and packaging it, are at:
| + | 1. In field ID, enter the unique id that will identify the plugin. Generally, we use the project name entered in the previous step : <tt>fr.systerel.rodinextension.sample</tt>, |
| − | http://sourceforge.net/p/rodin-b-sharp/CodeGen/ci/master/tree/TEB2FMI/ with
| + | 2. The version identify, the current plugin version. This field can be later updated via the MANIFEST file. We let the default value <tt>1.0.0.qualifier</tt>, |
| | + | 3. In the field Name, put the name of the plugin, here Qualitative Probabilistic Reasoning Plugin, |
| | + | 4. In the provider field, you can put the name of your company or insitution, |
| | + | 5. Ensure that the Execution Environment used is Java 1.6 (the one used by the Rodin Platform v.2.0), |
| | + | 6. Enter the class name of the plugin activator, preceded by its containing package. The activator is the static class responsible of the plugin lifecycle (start, stop, etc.). |
| | + | 7. Click on "'''Finish'''" |
| | | | |
| − | The templates feature.
| + | === What we got === |
| − | http://sourceforge.net/p/rodin-b-sharp/CodeGen/ci/master/tree/Templates/ .
| + | [[Image:Extend_Rodin_Tuto_1_4_ProjectExplorer1.png]] |
| | + | Eclipse created the plugin structure that we will be able to use to extend Rodin. |
| | | | |
| − | Code generation plug-ins have dependencies on [http://www.stups.hhu.de/ProB/index.php5/ProB_Java_API ProB2], which at this time, is still under development; and [https://github.com/snursmumrik/rms2/tree/multisim Component Diagrams]
| + | {{Navigation|Previous= [[Introduction_(How_to_extend_Rodin_Tutorial)|Introduction]] | Up= [[Plug-in_Tutorial|How to extend Rodin Tutorial (Index)]] | Next= [[Extend_Rodin_database_(How_to_extend_Rodin_Tutorial)|Extend the database]]}} |
| | | | |
| − | == Code Generation Feature - Version 0.2.5 for Rodin 2.8 ==
| + | [[Category:Developer documentation|*Index]] |
| − | 29 August 2013
| + | [[Category:Rodin Platform|*Index]] |
| − | | + | [[Category:Tutorial|*Index]] |
| − | A new version of the Code Generation Plug-in is available. The tool has been updated to accommodate changes made to its plug-in dependencies. It has improved translators for generating Java code, including setting up the project with a Java Nature and Java builder. The Java Development Tool-kit (JDT) is required if you wish to make use of these facilities. We have also added automatic flattening of invariants, and events; and we automatically infer typing annotations and parameter directions. Therefore, a developer has to perform fewer steps to generate code from an appropriately constructed model.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The following information may be of use:
| |
| − | * A [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/Tasking_Event-B_Overview Tasking Event-B] Overview.
| |
| − | * Generating code using [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/State-Machines_and_Code_Generation state-machine] diagrams.
| |
| − | * The use of [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/The_Use_of_Theories_in_Code_Generation Theories] in Code Generation.
| |
| − | ** Example Theories can be found in MathExtension the [https://github.com/andyed2003/codeGenTheoryRepo Git] repository, or clone [https://github.com/andyed2003/codeGenTheoryRepo.git this].
| |
| − | * A tutorial showing an example of specification, refinement, decomposition, Tasking Event-B, and theories for code generation can be found [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/Tasking_Event-B_Tutorial here].
| |
| − | ** The models used in the tutorial are available from the [https://github.com/andyed2003/codeGenExamples Git] repository or clone [https://github.com/andyed2003/codeGenExamples.git this].
| |
| − | * The sources for this version are available here [http://sourceforge.net/p/rodin-b-sharp/svn/15884/tree/tags/CodeGeneration/0.2.5.rodin2.8/ SVN]
| |
| − | * The lastest code generator source is available here: [http://sourceforge.net/p/rodin-b-sharp/svn/15819/tree/trunk/CodeGeneration SVN]
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Code Generation Feature - Version 0.2.3 for Rodin 2.7 ==
| |
| − | 04 Dec 2012. Update
| |
| − | | |
| − | We discovered a compatibility issue wrt the machine-generated Event-B model of the implementation. This occurs when Event-B is generated using the pop-up menu: Code Generation/Create Event-B build errors. The adjacent menu item (remove generated Event-B) can remove the Event-B that causes the errors.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The error occurs due to recently introduced static checks; these flag duplicate variable names in composed (but separate) machines as an error. We plan to release a fix for this problem in due course.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The problem does not effect the generation of code, once the errors have been fixed.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Example Projects and Theories, as below.
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Code Generation Feature - Version 0.2.3 for Rodin 2.5==
| |
| − | We released the latest Code generation Feature on 30th May 2012.
| |
| − | | |
| − | New features include:
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Code generation from [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/State-Machines_and_Code_Generation state-machine] diagrams.
| |
| − | * Improved static checking.
| |
| − | | |
| − | We have also provided some details of the [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/The_Use_of_Theories_in_Code_Generation use of Theories in code generation], from the previous version.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Updated Examples etc. are available:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * Tutorial, and example, projects are available from the Examples directory: [https://codegenerationd.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/codegenerationd/Examples/v0.2.3/ SVN].
| |
| − | * Test projects are also available from the Examples directory [https://codegenerationd.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/codegenerationd/Examples/v0.2.3/Tests SVN].
| |
| − | * Sources (will be) available at: [https://rodin-b-sharp.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/rodin-b-sharp/trunk/CodeGeneration SVN]
| |
| − | * Example Theories at: [https://codegenerationd.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/codegenerationd/Examples/TheoriesForCG SVN]
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Code Generation Feature - Version 0.2.2 for Rodin 2.4==
| |
| − | | |
| − | We released V0.2.2 on 22-03-2012. The main changes, to the interface, and translation from theories are described below:
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Tasking Event-B is now integrated with the Event-B Editors.
| |
| − | * We have the ability to translate to C, Java, etc. in addition to Ada source code.
| |
| − | * We use theories to define translations of the Event-B mathematical language (Theories for Ada, Java and C are supplied).
| |
| − | * We use the theory plug-in as a mechanism for defining new data types , and the translations to target data types.
| |
| − | * The translator is extensible.
| |
| − | * Minimal use is made of the EMF tree editor in Rose.
| |
| − | | |
| − | To install v0.2.2:
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Access the main Rodin Update Site. In Eclispe click on Help/Install new Software. Find the Rodin update site from the list. In Utilities add Code Generation.
| |
| − | The approach makes use of the following, which should be installed if the features are required by the user for editing:
| |
| − | *Model Decomposition: Download from the main Rodin Update Site, in the Decomposition section.
| |
| − | *Shared Event Composition: Download from the main Rodin Update Site, in the Decomposition section.
| |
| − | *Theory Plug-in: Download from the main Rodin Update Site, in the Modelling Extensions section.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Examples available at:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * Tutorial, and example, projects are available from the Examples directory: [https://codegenerationd.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/codegenerationd/Examples/v0.2.2/ SVN].
| |
| − | * Test projects are also available from the Examples directory [https://codegenerationd.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/codegenerationd/Examples/v0.2.2/CG_v0.2.2_Tests SVN]. | |
| − | * Sources at: [https://rodin-b-sharp.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/rodin-b-sharp/trunk/CodeGeneration SVN]
| |
| − | * Example Theories at: [https://codegenerationd.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/codegenerationd/Examples/TheoriesForCG SVN]
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Code Generation Feature - Version 0.2.1 for Rodin 2.3==
| |
| − | Contains Bug Fixes for previous release. 14-12-2011
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Code Generation Feature - Version 0.2.0 for Rodin 2.3==
| |
| − | We released a new version of the code generator on 30-11-2011, and updated documentation.
| |
| − | ===== Changes to the Tooling and Approach =====
| |
| − | The main changes are:
| |
| − | * The code generators have been completely re-written. The translators are now implemented in Java, i.e. there is no longer a dependence on the Epsilon tool set. This was undertaken for code maintenance reasons.
| |
| − | * Tasking Event-B is now integrated with the Event-B explorer.
| |
| − | * The Rose Editor is used for editing the Tasking Event-B, and
| |
| − | * a text-based editor is provided, using the Rose extension, for editing the TaskBody. This feature has been added to address some of the usability concerns. It also overcomes the 'problem' experienced with duplicate event names in a development, since the parser-builder that has been implemented automatically selects the correct event.
| |
| − | * The EMF tree editor in Rose is only used minimally; we plan enhancements to further reduce its use.
| |
| − | * Composed machines are used to store event 'synchronizations'; these are generated automatically during the decomposition process. This reduces the amount of typing in the TaskBody editor, since we no longer need to specify both local and remote (synchronizing) events.
| |
| − | * The code generation approach is now extensible; new target language constructs can be added using the Eclipse extension mechanism.
| |
| − | * The translation of target's mathematical language is now specified in the theory plug-in. This improves clarity since the the translation from source to target is achieved by specifying pattern matching rules. Extensibility is also improved; the theory plug-in is used to specify new data-types, and how they are implemented.
| |
| − | * Translated code is deposited in a directory in the appropriate files. An Ada project file is generated for use with AdaCore's GPS workbench. Eventually this could be enabled/disabled in a preferences dialog box.
| |
| − | * The Tasking Event-B to Event-B translator is now properly integrated. Control variable updates to the Event-B model are made in a similar way to the equivalent updates in the state-machine plug-in. The additional elements are added to the Event-B model and marked as 'generated'. This prevents users from manually modifying them, and allows them to be removed through a menu choice.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== Changes to the Documentation =====
| |
| − | The following Pages have been updated:
| |
| − | * [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/Tasking_Event-B_Overview Tasking Event-B Overview]
| |
| − | * [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/Tasking_Event-B_Tutorial Tutorial]
| |
| − | | |
| − | TODO
| |
| − | * Add addressed variables (for direct read/write access to memory)
| |
| − | * Flattening of composed machines/implementation machines.
| |
| − | * Interrupts
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Sensing and Actuating for Tasking Event-B ==
| |
| − | Version 0.1.5. Sensing and actuating events, and an Environ Machine have been added to allow simulation of the environment and implementation using memory mapped IO.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * The new v0.1.5 feature is available from the Rodin Update Site, it resides in the Utilities Category.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * As in previous releases, the code generation plug-in relies on the Epsilon tool suite. Add the following Epsilon interim update site to the list of available update sites in the Eclipse menu ''help/install new software'': http://download.eclipse.org/modeling/gmt/epsilon/interim/
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Select 'the Epsilon Core (Incubation)' component, this is the only component that is required for Tasking Event-B.
| |
| − | | |
| − | A new [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php?title=Tasking_Event-B_Tutorial Code Generation Tutorial] has been produced, that makes use of these new features. There is an explanation of the heating controller, upon which it is based, [http://wiki.event-b.org/index.php/Development_of_a_Heating_Controller_System here].
| |
| − | | |
| − | The example/tutorial projects, and also and a Bundled Windows 7 version, are available in the [http://deploy-eprints.ecs.soton.ac.uk/304/ Deploy E-Prints archive] or [https://codegenerationd.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/codegenerationd/Examples/HeatingController_Tutorial_v0.1.4/ Examples SVN site].
| |
| − | | |
| − | == The Code Generation Demonstrator for Rodin 2.1.x ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | Released 24 January 2011.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The Rodin 2.1.x compatible code generation demonstrator plug-ins have been released into the Rodin Sourceforge repository at:
| |
| − | | |
| − | https://rodin-b-sharp.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/rodin-b-sharp/trunk/CodeGeneration
| |
| − | | |
| − | The update-site is available through the Rodin update site in the ''Utilities'' category.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The code generation tutorial examples are available for download at:
| |
| − | | |
| − | https://sourceforge.net/projects/codegenerationd/files/DemoFiles/
| |
| − | | |
| − | The code generation plug-in relies on the Epsilon tool suite. Install Epsilon manually, since the automatic install utility does not seem to work for this feature. We currently use the Epsilon interim update site available at:
| |
| − | | |
| − | http://download.eclipse.org/modeling/gmt/epsilon/interim/
| |
| − | | |
| − | Select 'the Epsilon Core (Incubation)' component, this is the only component that is required for Tasking Event-B.
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Latest Developments ===
| |
| − | * Demonstrator plug-in feature version 0.1.0
| |
| − | ** for Rodin 2.1.x version is available.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * The Code Generation feature consists of,
| |
| − | ** a tasking Development Generator.
| |
| − | ** a tasking Development Editor (Based on an EMF Tree Editor).
| |
| − | ** a translator, from Tasking Development to Common Language Model (IL1).
| |
| − | ** a translator, from the Tasking Development to Event-B model of the implementation.
| |
| − | ** a pretty-printer for the Tasking Development.
| |
| − | ** a pretty-printer for Common Language Model, which generates Ada Source Code.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * A tutorial is available [[Code Generation Tutorial]]
| |
| − | ** Step 1 - Create the tasking development.
| |
| − | ** Step 2 - Add annotations.
| |
| − | ** Step 3 - Invoke translators.
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Ongoing Work ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Full Rodin Integration
| |
| − | * Sensed Variables
| |
| − | * Branching in Shared Machines
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Future Work ===
| |
| − | * Support for Interrupts.
| |
| − | * Richer DataTypes.
| |
| − | * Accommodation of duplicate event names in tasking developments.
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Metamodels ===
| |
| − | * In the plug-in we define several meta-models:
| |
| − | ** CompositeControl: for the control flow (algorithmic) constructs such as branch, loop and sequence etc. These constructs may be used in the specification of either sequential or concurrent systems.
| |
| − | ** Tasking Meta-model: defines the tasking model where we attach tasking specific details, such as task priority, task type. The tasking structures provide the ability to define single tasking or multi-tasking (concurrent) systems. We make use of the composite control plug-in to specify the flow of control. | |
| − | ** Common Language (IL1) Meta-model: defines an abstraction of common programming language constructs for use in translations to implementations.
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Translation Rules ===
| |
| − | * Tasking to IL1/Event-B translation rules [[http://wiki.event-b.org/images/Translation.pdf]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | == The Code Generation Demonstrator for Rodin 1.3.x ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | First release: 30 November 2010.
| |
| − | | |
| − | available from:
| |
| − | | |
| − | https://sourceforge.net/projects/codegenerationd/files/
| |
| − | | |
| − | The zip file contains a windows XP bundle, and a Windows V7 bundle. Alternatively, if you wish to build using an update-site, this is also included in the zip file, along with some notes on installation. However, note that the demonstrator tool is only compatible with Rodin 1.3.
| |
| − | | |
| − | A simple shared buffer example is provided. This will form the basis of a tutorial (which is work in progress). The WindowsBundles directory contains a Rodin 1.3.1 platform with the Code Generation plug-ins, together with a patch plug-in. The patch plug-in is required to correct an inconsistency in the org.eventb.emf.persistence plug-in. For the bundles, simply extract the appropriate zip file into a directory and run the rodin.exe. The plug-ins are pre-installed - the only configuration necessary may be to switch workspace to ''<installPath>\rodin1.3bWin7\workspace''. When using the update-site the example projects, and the project forming the basis of a simple tutorial, are provided in the accompanying zip file. These should be imported manually.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Mac users - no bundled version available at present, but use the update site in the 'advanced' folder.
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''A step-by-step [[Code Generation Tutorial]] is available'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==== About the Initial Release ====
| |
| − | The Code Generation (CG) Feature in the initial release is a demonstration tool; a proof of concept, rather than a prototype. The tool has no static checker and, therefore, there will be a heavy reliance on docs and dialogue to facilitate exploration of the tools and concepts.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==== Source Code ====
| |
| − | | |
| − | The sources are available from,
| |
| − | | |
| − | https://codegenerationd.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/codegenerationd
| |
| − | | |
| − | Note - I used Eclipse 3.5 Galileo, and you will need to install (or have sources from) Epsilon's interim update site. There is also dependency on Camille v2.0.0
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | [[Category:Work in progress]]
| |
| − | [[Category:User documentation]]
| |
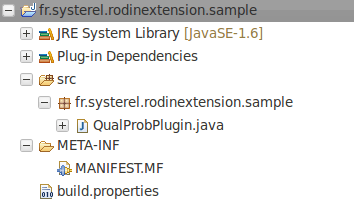 Eclipse created the plugin structure that we will be able to use to extend Rodin.
Eclipse created the plugin structure that we will be able to use to extend Rodin.