Generated Model Elements: Difference between revisions
imported>Nicolas |
imported>Nicolas m →Example: Added category Developer documentation |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
In the above example, we just clicked the remove button for 'axm3'. | In the above example, we just clicked the remove button for 'axm3'. | ||
[[Category:Developer documentation]] | |||
Revision as of 12:59, 12 October 2009
Various tools generate models (Decomposition, UML-B, ...). Editing a generated model is not recommended, as further model generations will simply override the modifications. Thus, generated models should not be modifiable by editors, and we need a way to tag these models and prevent editing. To that end, a new boolean attribute is defined: 'org.eventb.core.generated'. Tools can put this attribute on any internal element they generate; its presence is checked by editors so they can forbid editing tagged elements.
Convention
The semantics of the 'org.eventb.core.generated' attribute is defined as follows:
- if the attribute is absent, the element is considered not generated
- if the attribute is present with value 'false', idem
- if the attribute is present with value 'true', the attributed element and all its children (recursively) are considered generated
Thus, a given internal element is considered generated if any of the following holds:
- it has the 'org.eventb.core.generated' attribute with value 'true'
- one of its ancestors has the 'org.eventb.core.generated' attribute with value 'true'
Example
Let's see what it looks like when opening a generated model. In the following example, the root element is tagged generated, so all internal elements are read-only:
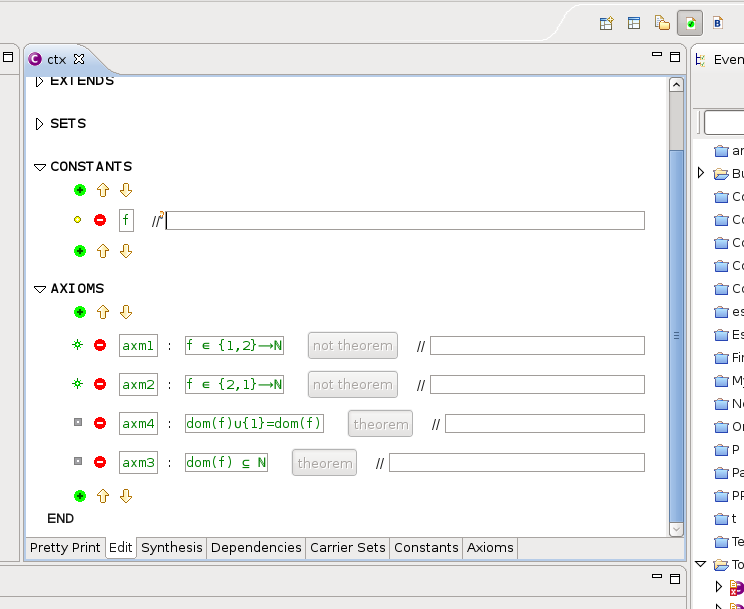
If we try to modify a text field or click a 'theorem' button, nothing happens. Attempts to add or remove elements fail with a popup message:
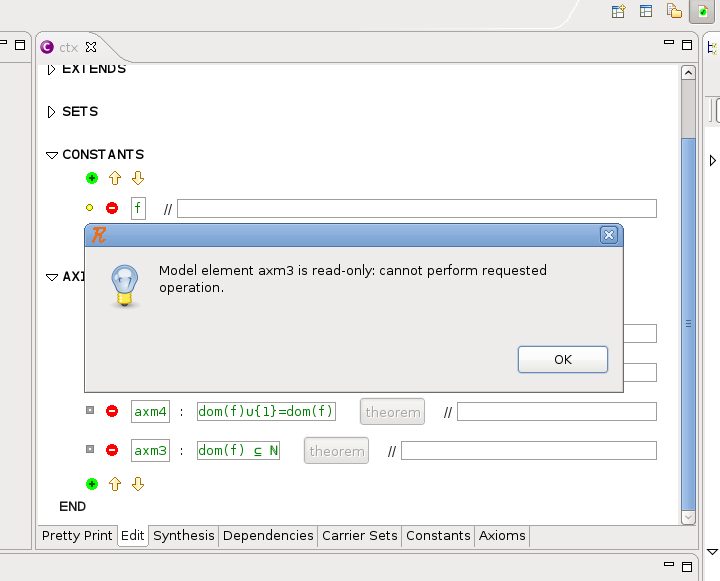
In the above example, we just clicked the remove button for 'axm3'.