Event Model Decomposition
Introduction
One of the most important feature of the Event-B approach is the possibility to introduce new events during refinement steps, but a consequence is an increasing complexity of the refinement process when having to deal with many events and many state variables.
The main idea of the decomposition is to cut a model  into sub-models
into sub-models  , which can be refined separately and more comfortably than the whole.
, which can be refined separately and more comfortably than the whole.
The constraint that shall be satisfied by the decomposition is that these refined models might be recomposed into a whole model 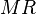 in a way that guarantees that
in a way that guarantees that 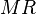 refines
refines  . Note that this recomposition will never be performed in practice.
. Note that this recomposition will never be performed in practice.
An event-based decomposition of a model is detailed in the Event Model Decomposition article: the events of a model are partitioned to form the events of the sub-models. In parallel, the variables on which these events act are distributed among the sub-models.
The purpose is here to precisely describe what is required at the Rodin platform level to integrate this event model decomposition, and to explain why. The details of how it could be implemented are out of scope.
Terminology
This section introduces the definitions of the main technical terms, which are widely used in the sequel.
- Event model decomposition: The decomposition of a model in sub-models, called A-style decomposition (after Abrial). The B-style decomposition (after Butler) is not considered here.
A model can contain contexts, machines, or both (see the modelling language). The notion of model decomposition covers on the one hand the machine decomposition, and on the other hand the context decomposition, both being interdependent.
- Sub-machine: A machine built from a non-decomposed machine during the event model decomposition.
- Sub-context: A context built from a non-decomposed context during the event model decomposition.
- Shared variable: A variable accessed by events of distinct sub-machines (by opposition to private variable). A variable is said to be shared between a sub-machine
 and a sub-machine
and a sub-machine 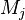 if and only if it is accessed by events of
if and only if it is accessed by events of  and by events of
and by events of 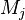 .
. - Private variable: A variable accessed by events of a single sub-machine (by opposition to shared variable).
- External event: An event of a sub-machine which is built from an event of the non-decomposed machine, and which simulates the way the shared variables (between this sub-machine and another sub-machine) are handled in the non-decomposed machine (by opposition to internal event).
- Internal event: An event copied from the non-decomposed machine to a sub-machine, according to the end-user specified distribution (by opposition to external event).
Note that a variable is said to be accessed when it is read or written. More precisely, such an access may be performed by a predicate (invariant, guard, witness) or in an assignment (action).
High-level Specification
The high-level specification details how the event model decomposition shall be integrated into the Rodin platform as a new feature, by linking to the existing architecture.
Definition of the decomposition
It is necessary to first give a definition of the event model decomposition in the Rodin platform. Is it an Event-B project decomposition? Or, is it a decomposition performed from some well-identified machines and contexts of a given Event-B project?
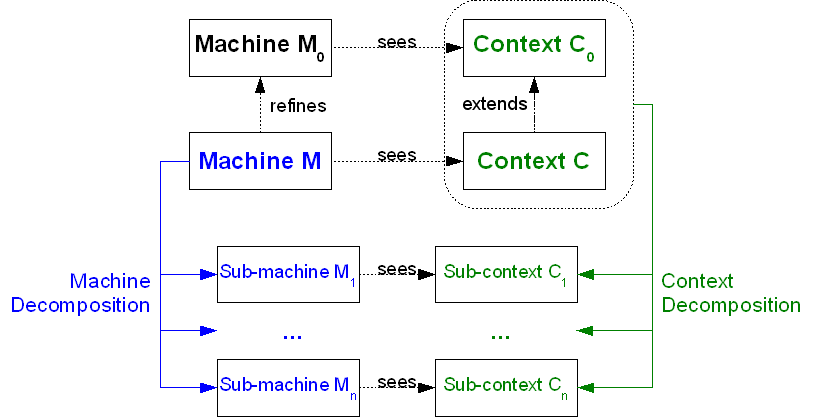
As illustrated in the diagram below, when considering a given Event-B project, the entry point for the decomposition is a machine  of the project, and its whole hierarchy of seen contexts. The machine
of the project, and its whole hierarchy of seen contexts. The machine  to be taken as input for the decomposition shall be pointed by the end-user.
to be taken as input for the decomposition shall be pointed by the end-user.
Configuration of the decomposition
The end-user shall be asked to parametrize the decomposition, and more precisely to:
- identify the machine to be taken as input for the decomposition.
- identify the sub-machines to be created.
- partition the events.
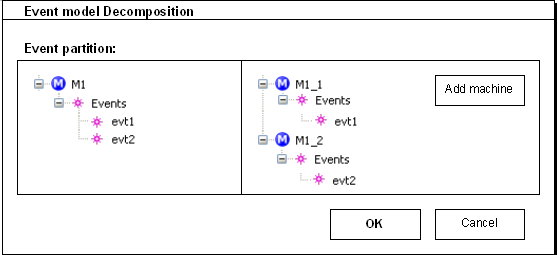
It is more suitable for the end-user to visualize the configuration, and as a consequence it shall preferably be performed through the Graphical User Interface of the Rodin platform.
The following dialog box, which fills these requirements, is given as an example. The left-hand side displays the non-decomposed model and the right-hand side the decomposed model. The second one is built by the user, by first adding machines and then copying events from left to right.
The end-user shall have a way to backup its configuration. More precisely, it shall be possible on the one hand to export a configuration to a file, and on the other hand to import a configuration from a file.
Execution of the decomposition
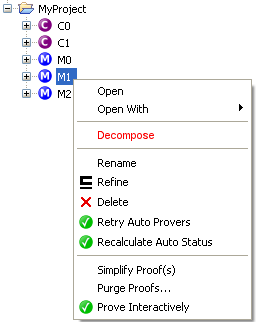
A Decompose action shall be added. It shall be enabled if and only if a machine is selected. It shall be available from the Project menu, from the toolbar, and in the contextual menu displayed when right-clicking on the selected project.
A new Event-B project shall be created for each sub-machine built during the configuration. The decomposition of the sub-machine shall first be completed, and then the non-decomposed context shall be partitioned.
The created projects and components (machines and contexts) shall be tagged as "automatically generated". It shall be possible to identify the non-decomposed machine from which they are issued.
As far as possible, the developments shall not be performed in the Event-B core; the dedicated extension points shall be used instead (eg. those provided for the static checker. See the plugin.xml file of the org.eventb.core package).
Generation of the proof obligations
A model to be decomposed is assumed to be proved, i.e. all the proof obligations (PO) have been handled successfully. The decomposition of a model shall otherwise be forbidden.
Moreover, the following conditions on PO shall be fulfilled during the decomposition:
- The decomposition shall not generate any new proof obligation.
- The proof obligations related to the non-decomposed model shall not be "propagated" to the decomposed models to be proved again. As a consequence, the Proof Obligation Generator (POG) shall be temporary disconnected until the decomposition is performed.
Low-level Specification
The low-level specification details through several steps how the event model decomposition shall be performed, and in which order. It establishes a distinction between the steps performed on the end-user's initiative, and the computed ones. It links when possible to the already implemented features of the Rodin platform which can be used at some steps.
The following sequence shall be observed to decompose a machine  in sub-machines
in sub-machines 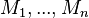 :
:
- The events of
 shall be partitioned in
shall be partitioned in 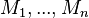 , as indicated by the end-user (see Event partition).
, as indicated by the end-user (see Event partition). - The Rodin platform shall update the status of the events (see Event status).
- The Rodin platform shall distribute the variables of
 in
in 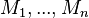 , according to the event partition (see Variable distribution).
, according to the event partition (see Variable distribution). - The Rodin platform shall distribute the invariants of
 in
in 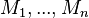 , according to the variable distribution (see Invariant distribution).
, according to the variable distribution (see Invariant distribution). - The Rodin platform shall build external events in
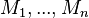 , from the events of
, from the events of  , and according to the variable distribution (see External event construction).
, and according to the variable distribution (see External event construction). - The Rodin platform shall build the initialization events of
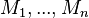 , according to the variable distribution (see Initialization event construction).
, according to the variable distribution (see Initialization event construction). - The Rodin platform shall build the contexts seen by
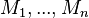 , from the hierarchy of contexts associated to
, from the hierarchy of contexts associated to  (see Context decomposition).
(see Context decomposition).
This order will be justified by itself subsequently, when going into the details of the decomposition.
Decomposition of a machine in sub-machines
The purpose of this paragraph is to precisely describe how to decompose  .
.
The refinement hierarchy for  (see the
(see the 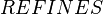 clauses) shall not be considered for the decomposition. A sub-machine
clauses) shall not be considered for the decomposition. A sub-machine  may indeed be seen as a new abstract machine, which may be later refined if necessary. It is necessary to keep this assumption in mind when decomposing
may indeed be seen as a new abstract machine, which may be later refined if necessary. It is necessary to keep this assumption in mind when decomposing  .
.
About the variables
Some variables are needed by several sub-machines of the decomposition. As a consequence, these variables shall be replicated in the sub-machines. Beyond that, since it is not possible to ensure that such a variable will be refined in the same way in each sub-machine, they shall be given a special status (shared variable), with the limitation that they cannot be refined.
We will specify in this section how to introduce the notion of shared variable in the Rodin platform, and how to check the associated rules.
The following DTD excerpt describes the structure of a variable in the Rodin database:
<!ENTITY % NameAttDecl "name CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ENTITY % CommentAttDecl "org.eventb.core.comment CDATA #IMPLIED"> <!ENTITY % IdentAttDecl "org.eventb.core.identifier CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ELEMENT %variable; EMPTY> <!ATTLIST %variable; %NameAttDecl; %CommentAttDecl; %IdentAttDecl; >
A first possibility to tag a variable as shared would be to add a shared specific attribute, which would be set to true if and only if the variable is shared:
<ENTITY % shared "org.eventb.core.shared CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ELEMENT %variable; EMPTY> <!ATTLIST %variable; ... %shared; (false|true) #REQUIRED >
Another possibility would be to define a more generic attribute, which could take different values, according to the nature of the variable:
<ENTITY % nature "org.eventb.core.nature CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ATTLIST %variable; ... %nature; (0|1) #REQUIRED >
The second option, which has the main advantage to be more scalable, is retained here.
A shared variable shall always be present in the state space of any refinement of the component. The verification shall be added to those already performed by the static checker. The static checker shall have a way to determine if a given variable is shared or not.
Distributing the variables in the sub-machines of the decomposition
The first question raised by the distribution of the variables is whether it shall be the first stage of the decomposition, or not. Let's first suppose that the answer is "yes". The case where  is an event that accesses a variable
is an event that accesses a variable 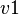 associated to a sub-machine
associated to a sub-machine  and a variable
and a variable 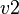 associated to a sub-machine
associated to a sub-machine  cannot be successfully handled: should
cannot be successfully handled: should  be associated to
be associated to  or to
or to  ? Moreover, contrary to the events, the variables are not essentially bearers of meanings, and they cannot by themselves guide the decomposition.
? Moreover, contrary to the events, the variables are not essentially bearers of meanings, and they cannot by themselves guide the decomposition.
As a consequence, it is pertinent to assume that the events have been first partitioned. The following cases have then to be taken into consideration when dealing with the variable distribution:
- If
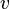 is a variable that is only accessed by events of a given sub-machine
is a variable that is only accessed by events of a given sub-machine  , then
, then 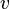 is a private variable of
is a private variable of  . It shall be moved to
. It shall be moved to  .
. - If
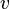 is a variable that is accessed by events of distinct sub-machines
is a variable that is accessed by events of distinct sub-machines 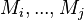 , then
, then 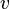 is a shared variable. It shall be tagged as such and duplicated in all sub-machines.
is a shared variable. It shall be tagged as such and duplicated in all sub-machines.
If all the variables are shared at the conclusion of the distribution, the end user shall be notified (it certainly means that the decomposition was not judicious!).
Propagating the sharing status
A variable tagged as shared in the non-decomposed machine (when resulting from a previous decomposition) shall remain shared in the sub-machines.
About the events
It shall be possible to simulate the way the shared variables are handled in the non-decomposed machine. This is precisely the purpose of the so-called external events.
We will examine in this section how to define such events in the Rodin platform, how to construct them, and how to enforce the rules that apply (in particular, these events cannot be refined).
Partitioning the events in the sub-machines of the decomposition
The sub-machines 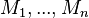 shall be built and the events of
shall be built and the events of  shall be partitioned in these newly created machines, according to the end-user configuration. The initialization event of
shall be partitioned in these newly created machines, according to the end-user configuration. The initialization event of  shall be left out. All other events shall be distributed.
shall be left out. All other events shall be distributed.
At this step, the sub-machines shall only contain these internal events. In particular, the 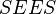 and
and 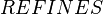 clauses of
clauses of 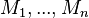 shall be empty. In the same manner, the
shall be empty. In the same manner, the 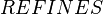 and
and 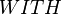 (witnesses) clauses of the events shall be left out.
(witnesses) clauses of the events shall be left out.
If an event has the extended status (i.e. it inherits the actions of the refined event), then it shall first be merged with the refined event before being copied in the sub-machine. Note that such a merge is performed by the pretty printer of the Rodin platform (compare the information displayed, on the one hand in the "Pretty Print" view, and on the other hand in the "Edit" view, for an extended event).
Propagating the event status
The convergence status of a given event shall be propagated in the sub-machines as described below:
- An event tagged as ordinary in the non-decomposed machine shall remain ordinary in the sub-machine.
- An event tagged as convergent in the non-decomposed machine shall become ordinary in the sub-machine.
- An event tagged as anticipated in the non-decomposed machine shall remain anticipated in the sub-machine.
- An external event shall always be declared as ordinary.
See the modelling language for precisions on the convergence status.
In the same manner, an event (internal or external) of a sub-machine shall always be declared as non-extended.
An event tagged as external in the non-decomposed machine (when resulting from a previous decomposition) shall remain external in the sub-machine.
Identifying an event as external
An attribute is already defined, which is introduced below, to precise the nature of an event. A first solution would be to add another masked value (eg. 4) to encode the external status.
<!ENTITY % convergence "org.eventb.core.convergence"> <!ATTLIST %event; ... %convergence; (0|1|2) #REQUIRED ... >
Another solution would be to add a distinct external attribute, which would be set to true if and only if the event is external:
<ENTITY % external "org.eventb.core.external CDATA #REQUIRED"> <!ATTLIST %event; ... %external; (false|true) #REQUIRED >
This solution is preferred because the notion of external event is totally orthogonal to the notion of convergence.
Ensuring that an external event is not refined
If a machine  refines a sub-machine
refines a sub-machine  , several verifications shall be performed by the static checker to ensure that the external events defined in
, several verifications shall be performed by the static checker to ensure that the external events defined in  are not refined in
are not refined in  . In other terms, they shall be strictly identical in
. In other terms, they shall be strictly identical in  and
and  :
:
- For each external event of
 ,
,  shall define an event with the same name.
shall define an event with the same name. - This event shall have a REFINES clause pointing to the event itself.
- This event shall have the extended status.
- This event shall not declare any additional element (parameter, guard, witness or action).
The verifications shall be performed by the static checker. The static checker shall have a way to determine if a given event is external or not.
With the introduction of theorem in guard, "extended" status will cause problem since ones required to prove again the theorem in guard at every refinement level. As far as I can see, there are two different possibilities:
- Changing all the theorems in guard into actual guards.
- Change the POG to disable the PO generation for proving theorem in guard for external events.
I (Son) think the first option is better and easier to implement.
Constructing an external event
If  is an event that modifies a shared variable
is an event that modifies a shared variable  (i.e.
(i.e.  is listed among the free identifiers on the left-hand side of an assignment), then an external event that modifies
is listed among the free identifiers on the left-hand side of an assignment), then an external event that modifies  shall be built from
shall be built from  in each sub-machine where
in each sub-machine where  is accessed.
is accessed.
The construction of an external event depends on the source machine (i.e. the sub-machine containing the event  from which the external event is to be built) and on the destination machine (i.e. the sub-machine where the external event is to be built).
from which the external event is to be built) and on the destination machine (i.e. the sub-machine where the external event is to be built).
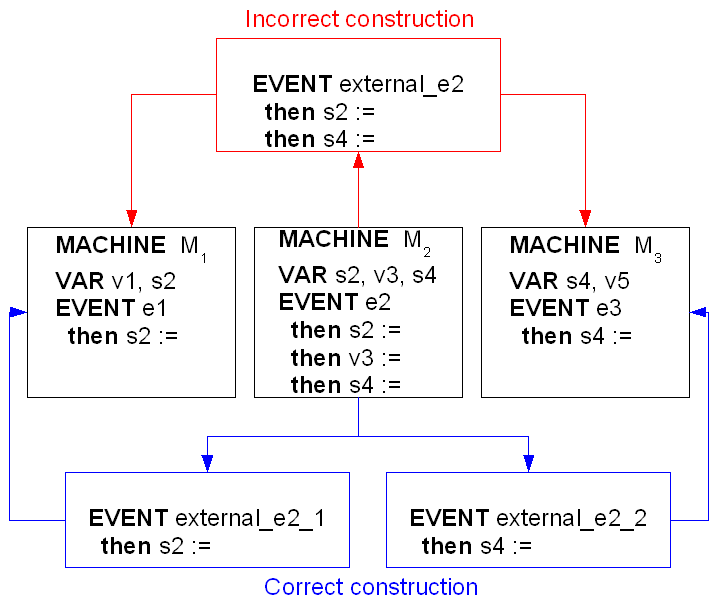
Building an external event from a given event  modifying a shared variable
modifying a shared variable  and duplicating it in each sub-machine where
and duplicating it in each sub-machine where  is accessed is indeed incorrect, as illustrated below: the sub-machine
is accessed is indeed incorrect, as illustrated below: the sub-machine  does not know the shared variable
does not know the shared variable 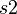 and the sub-machine
and the sub-machine  does not know the shared variable
does not know the shared variable 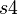 .
.
The construction of an external event highly relies on some rewriting rules. It is recommended to peruse them before reading further.
 is an internal event of the source machine
is an internal event of the source machine 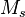 ,
, 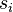 are variables shared between
are variables shared between 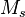 and the destination machine
and the destination machine 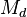 ,
, 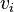 are other variables (private to
are other variables (private to 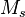 or shared between
or shared between 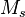 and another sub-machine, distinct from
and another sub-machine, distinct from 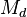 ),
), 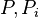 are before-after predicates, and
are before-after predicates, and 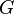 is a predicate.
is a predicate.
Generic construction
We first focus on the generic construction of an external event from an internal event whose action is expressed as follows:
e WHERETHEN
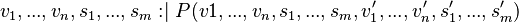
- The first step of the construction consists in replacing the
 variables by parameters. Note that this step is purely fictive, because assigning an event parameter is not allowed!
e
ANY
variables by parameters. Note that this step is purely fictive, because assigning an event parameter is not allowed!
e
ANY - The second step consists in adding guards to define the types of the parameters, if necessary. More precisely, a theorem shall be added for each parameter for which typing is required. The .bcm file associated to the non-decomposed machine shall be parsed in order to retrieve the typing information.
- The third and last step of the construction consists in introducing an existential quantifier to resolve the invalid assignment.
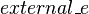 is the newly built external event.
external_e
ANY
is the newly built external event.
external_e
ANY
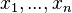 WHERE
WHERE
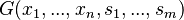 THEN
THEN
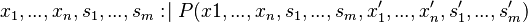
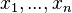 WHERE
WHERE
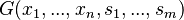 THEN
THEN
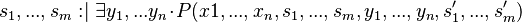
Derived constructions
Then, it is possible to derive the construction for other actions:
- Each assignment of the action shall be handled separately (see transformation rules on Event-B actions).
- The transformation rules shall be applied on each Event-B assignment.
Example
e WHERETHEN
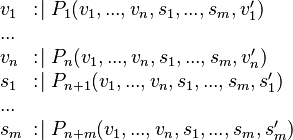
external_e ANYWHERE
THEN

Decomposing the initialization event
An initialization event shall be built in each sub-machine from the initialization event of the non-decomposed machine, and according to the distribution of the variables among these sub-machines. The construction is detailed below. 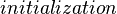 is the initial event and
is the initial event and  the built event,
the built event, 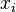 are variables (private or shared) of the sub-machine containing
are variables (private or shared) of the sub-machine containing  ,
, 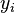 are variables of other sub-machines, and
are variables of other sub-machines, and 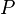 is a predicate.
is a predicate.
initialization THEN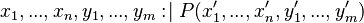
Only the variables of the considered sub-machine shall appear in the built initialization event; other variables shall become bound:
e THEN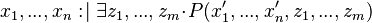
The derived cases and simplification rules introduced during the construction of the external events apply here as well.
If  refines a sub-machine
refines a sub-machine  issued from the decomposition of a machine
issued from the decomposition of a machine  , the initialization event of
, the initialization event of  shall not constrain a shared variable more or less than it was in the initialization event of
shall not constrain a shared variable more or less than it was in the initialization event of  .
.
An initialization event shall not contain an action modifying at the same time a shared variable and a private variable (eg. 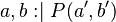 , where
, where 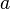 is private and
is private and 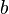 is shared). If such a behavior was authorized, a two-way simulation proof obligation would indeed be necessary to ensure that the shared variable is not constrained differently in further refinements. As a consequence, the decomposition of
is shared). If such a behavior was authorized, a two-way simulation proof obligation would indeed be necessary to ensure that the shared variable is not constrained differently in further refinements. As a consequence, the decomposition of  shall be forbidden if its initialization event contain such an action. Moreover, the static checker shall ensure that the initialization event of
shall be forbidden if its initialization event contain such an action. Moreover, the static checker shall ensure that the initialization event of  does not contain such an action.
does not contain such an action.
Finally, the static checker shall ensure that the actions of the initialization event of  related to the shared variables are not modified in
related to the shared variables are not modified in  . More precisely, the actions shall be syntactically equal.
. More precisely, the actions shall be syntactically equal.
About the invariants
We will see in this section how to distribute the invariants among the sub-machines, once the variables have been distributed.
An invariant based on a 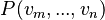 predicate shall be copied in a sub-machine
predicate shall be copied in a sub-machine  if and only if
if and only if  contains the
contains the 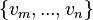 variables.
variables.
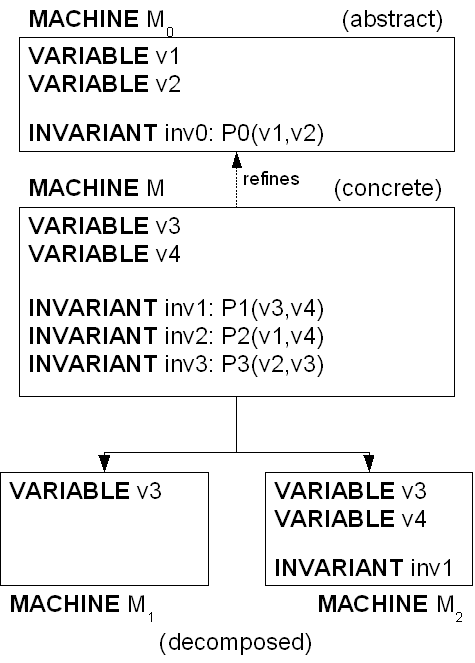
This distribution is illustrated in the figure below, where  is an abstract machine,
is an abstract machine,  is a concrete machine extending
is a concrete machine extending  ,
,  and
and  are the sub-machines resulting from the decomposition of
are the sub-machines resulting from the decomposition of  .
. 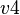 is a private variable of
is a private variable of  ,
, 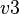 is a variable shared between
is a variable shared between  and
and  , and
, and 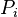 are predicates.
are predicates.
If an invariant is used for typing but it has not been copied, a theorem shall be added in the sub-machines for each variable for which typing is required (otherwise a problem will be detected by the static checker). Note that there is no contradiction with the requirements on proof obligations; no proof obligation (PO) is indeed generated for predicates 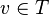 , where
, where 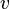 is a variable and
is a variable and 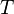 is a type.
is a type.
In the same manner, if an invariant is used for well-definedness but is has not been copied, a theorem shall be added in the sub-machines. The associated proof obligation is the well-definedness (WD) obligation, and it is assumed to be proved; as a consequence, it does not have to be generated in the sub-machines.
For example, let  be a constant.
be a constant. 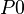 ,
, 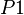 and
and 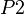 are defined as follows:
are defined as follows:
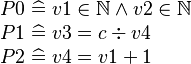
A theorem shall be added to indicate that 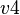 is not null.
is not null.
The org.event.core.ast.Formula.getWDPredicate method shall be used to compute the WD predicate associated to a given predicate. If no WD predicate is required, this method returns true. The built WD predicate shall be inserted before the associated predicate in the list of invariants of the considered sub-machine.
Beyond that, a workaround exists if an invariant 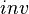 , based on a
, based on a 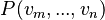 predicate, seems useful (for example an invariant between a concrete variable and some abstract variable) but it has disappeared in a sub-machine
predicate, seems useful (for example an invariant between a concrete variable and some abstract variable) but it has disappeared in a sub-machine  containing variables
containing variables 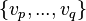 (eg.
(eg. 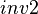 and
and 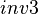 have both been excluded from the sub-machines by application of the stated rules). It is indeed possible to add in the non-decomposed machine a theorem based on
have both been excluded from the sub-machines by application of the stated rules). It is indeed possible to add in the non-decomposed machine a theorem based on 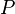 , but where the variables
, but where the variables 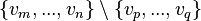 become bound, and then to perform again the decomposition. It will lead to a new proof obligation in the non-decomposed machine, which does not pose any difficulty.
become bound, and then to perform again the decomposition. It will lead to a new proof obligation in the non-decomposed machine, which does not pose any difficulty.
For example, if a theorem 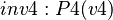 , with
, with 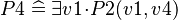 , is added to the
, is added to the  concrete machine, then it will be copied in the sub-machine
concrete machine, then it will be copied in the sub-machine  during the decomposition. In order to prove the
during the decomposition. In order to prove the 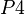 statement, the bound variable
statement, the bound variable 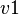 shall obviously be instantiated with
shall obviously be instantiated with 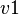 .
.
About the variants
As mentioned before, there is no convergent event in sub-machines. As a consequence, there is no need to take the variants into consideration when performing the decomposition.
Decomposition of a context in sub-contexts
The purpose of this paragraph is to specify how to decompose a context, according to the decomposition of a given machine  , and to establish how to link the sub-contexts to the sub-machines.
, and to establish how to link the sub-contexts to the sub-machines.
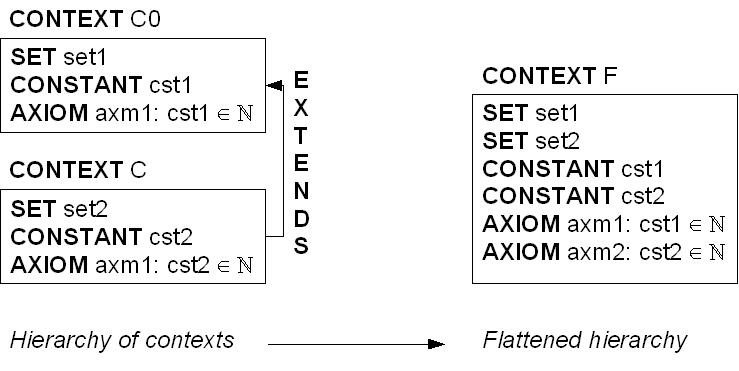
The hierarchy of contexts (see the 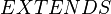 clauses of contexts and the
clauses of contexts and the 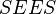 clause of
clause of  ) shall be first accumulated in a single context. More precisely, a new context
) shall be first accumulated in a single context. More precisely, a new context 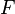 shall be built (virtually or not), which contains all the carrier sets, constants and axioms of the hierarchy. This context is assumed to be the non-decomposed context from which the sub-contexts
shall be built (virtually or not), which contains all the carrier sets, constants and axioms of the hierarchy. This context is assumed to be the non-decomposed context from which the sub-contexts 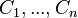 shall be built.
shall be built.
Note that it may be necessary to rename some axioms when flattening the hierarchy.
Then, an empty context 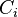 shall be built for each sub-machine
shall be built for each sub-machine  , by respecting the following sequence: the constants shall be first included, then the carrier sets shall be added, and finally the axioms shall be considered.
, by respecting the following sequence: the constants shall be first included, then the carrier sets shall be added, and finally the axioms shall be considered.
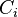 shall be linked to
shall be linked to  through its
through its 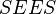 clause. Note that, at the conclusion of the context decomposition, the sub-contexts
clause. Note that, at the conclusion of the context decomposition, the sub-contexts 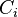 that may be empty shall not be kept, and a
that may be empty shall not be kept, and a 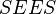 clause shall not be added to the associated sub-machines
clause shall not be added to the associated sub-machines  .
.
About the constants
A constant of a non-decomposed context 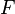 shall be copied in a sub-context
shall be copied in a sub-context 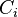 if and only if it appears in a predicate (invariant or guard) or in an assignment (action) of the associated sub-machine
if and only if it appears in a predicate (invariant or guard) or in an assignment (action) of the associated sub-machine  .
.
Thus, if a constant is not accessed by a sub-machine (e.g. if such a constant was only accessed by an abstract machine extended by the non-decomposed machine), then it shall be left out during the decomposition. In parallel, if a constant is accessed by distinct sub-machines, then it shall be duplicated in the associated sub-contexts.
About the carrier sets
A carrier set shall be visible from any sub-machine  which accesses it, explicitly or implicitly, through a predicate or an assignment. In other terms, a carrier set of a non-decomposed context
which accesses it, explicitly or implicitly, through a predicate or an assignment. In other terms, a carrier set of a non-decomposed context 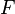 shall be copied in a sub-context
shall be copied in a sub-context 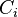 if and only if this set appears in a predicate or assignment of the associated sub-machine
if and only if this set appears in a predicate or assignment of the associated sub-machine  , or types a constant previously copied to
, or types a constant previously copied to 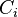 .
.
As for the constants, a carrier set may be left out or duplicated.
About the axioms
We will see in this section how to distribute the axioms among the sub-contexts, once the constants and carrier sets have been copied.
As for the invariants, an axiom is copied in a sub-machine  if and only if
if and only if  contains the referenced constants and sets. If an axiom is used for typing but it has not been copied, a theorem shall be added in the sub-contexts for each constant for which typing is required (otherwise a problem will be detected by the static checker).
contains the referenced constants and sets. If an axiom is used for typing but it has not been copied, a theorem shall be added in the sub-contexts for each constant for which typing is required (otherwise a problem will be detected by the static checker).
Mathematical Approach
The purpose of this section is to mathematically formalize the Event-B decomposition previously specified, and by the way to remove the possible remaining ambiguity.
Let's define 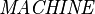 as the set of all machine handles,
as the set of all machine handles, 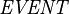 the set of all events, and
the set of all events, and 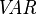 the set of all variables.
the set of all variables.
- The partition of the events of the non-decomposed machine among the different sub-machines (according to the end-user configuration) can be represented with a partial function:
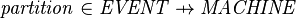
For a given sub-machine 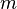 ,
, ![partition^{-1}[\{m\}]~](/images/math/5/3/6/536e2ff3c96a2862a0983a2aeac5fd71.png) is then the set of internal events of
is then the set of internal events of 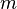 .
.
- The access of a variable by a given event (according to the static-checker) can be expressed as:
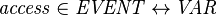
For a given variable 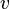 ,
, ![(partition;access^{-1})[\{v\}]~](/images/math/5/d/e/5de315fbfd96dba196a6bbc9e027ca80.png) is then the set of the sub-machines accessing
is then the set of the sub-machines accessing 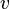 , and
, and 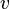 is a private variable of a sub-machine
is a private variable of a sub-machine 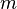 if and only if this set contains a single component (i.e.
if and only if this set contains a single component (i.e. ![card((partition;access^{-1})[\{v\}]) = 1~](/images/math/6/6/2/662b31399292b3d36f645566a3977053.png) ); otherwise, and if and only if this set is not empty,
); otherwise, and if and only if this set is not empty, 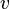 is shared.
is shared.
In parallel, for a given sub-machine 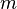 ,
, ![(access;partition^{-1})[\{m\}]~](/images/math/7/9/a/79a283c44307ac8e522c1ee8dbc80bf7.png) is the set of variables accessed by the events contained in
is the set of variables accessed by the events contained in 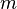 .
.
- The association of a variable with the events modifying this variable (according to the static-checker) can be specified as:
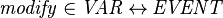
For a given sub-machine 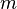 and a variable
and a variable ![v \in (access;partition^{-1})[\{m\}]](/images/math/4/1/7/4172a0084bd6cea0545a132d49c7c26e.png) ,
, ![modify[\{v\}]~](/images/math/a/8/5/a85b30e0e7d704f1116ba44a4299390c.png) is then the set of the events modifying
is then the set of the events modifying 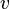 .
.
- The construction of the external events for a sub-machine can be represented with a relation:
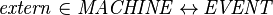
It is computed as follows: 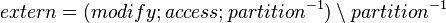
Thus, the external events of a given sub-machine 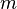 are events modifying the variables accessed by the internal events of
are events modifying the variables accessed by the internal events of 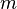 , but they are not internal events of
, but they are not internal events of 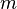 .
.
Example
The following example is taken from the Event Model Decomposition.
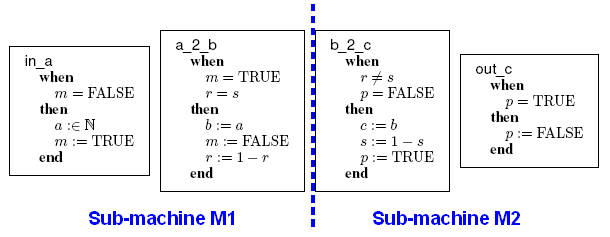
A non-decomposed machine has been decomposed in two sub-machines  and
and  , as illustrated by the figure.
, as illustrated by the figure.
According to the terminology, 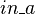 and
and 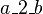 are internal events of
are internal events of  , and
, and 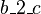 and
and 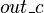 are internal events of
are internal events of  . Concerning the variables,
. Concerning the variables, 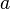 and
and 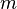 are private variables of
are private variables of  ,
,  and
and 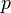 are private variables of
are private variables of  , and
, and 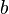 ,
,  and
and  are shared variables.
are shared variables.
The variables accessed by the internal events of  are
are 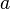 ,
, 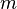 ,
, 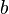 ,
,  and
and  . The events modifying these variables are
. The events modifying these variables are 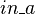 ,
, 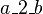 , which both are internal events of
, which both are internal events of  , and
, and 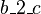 , which is an internal event of
, which is an internal event of  . Thus, according to the definition given above,
. Thus, according to the definition given above, 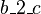 is an external event for
is an external event for  . In the same manner,
. In the same manner, 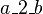 is an external event for
is an external event for  .
.
N.B.: Note that the expression "is an external event for" is an extrapolation, and shall be literally interpreted as "should lead to the construction of an external event in".
Example
It seems to be interesting to illustrate the decomposition step by step through an example. The considered example is described in the Event Model Decomposition.
The QuestionResponse.zip archive file contains the corresponding QuestionResponse Rodin project, and in particular the  machine taken as input for the decomposition. The QuestionResponse_i projects are issued from the decomposition and respectively contain the
machine taken as input for the decomposition. The QuestionResponse_i projects are issued from the decomposition and respectively contain the  ,
,  and
and  sub-machines.
sub-machines.
The events
The events of  are partitioned among
are partitioned among  ,
,  and
and  , as illustrated below:
, as illustrated below:
- The
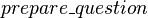 event is an internal event of
event is an internal event of  .
. - The
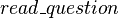 and
and 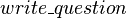 events are internal events of
events are internal events of  .
. - The
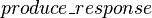 event is an internal event of
event is an internal event of  .
.
The variables
The status (private or shared) of the variables is given below:
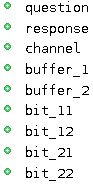
- is a private variable of
 .
. - is a private variable of
 .
. - is a private variable of
 .
. - is shared between
 and
and  .
. - is shared between
 and
and  .
. - is shared between
 and
and  .
. - is shared between
 and
and  .
. - is shared between
 and
and  .
. - is shared between
 and
and  .
.
The distribution of the variables follows:
- The
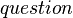 ,
, 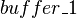 ,
, 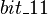 and
and 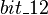 variables are copied in
variables are copied in  .
. - The
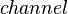 ,
, 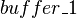 ,
, 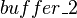 ,
, 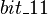 ,
, 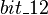 ,
, 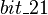 and
and 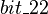 variables are copied in
variables are copied in  .
. - The
 ,
, 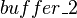 ,
, 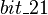 and
and 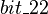 variables are copied in
variables are copied in  .
.
The invariants
The defined invariants are copied:

- is copied in
 and
and  .
. - is copied in
 and
and  .
. - is discarded, because it refers to an unknown variable (
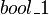 ).
). - is copied in
 and
and  .
. - is copied in
 and
and  .
. - is discarded, because it refers to an unknown variable (
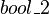 ).
).
The missing typing theorems are added. The typing information is extracted from the QuestionResponse.bcm file:
- The
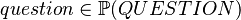 theorem is added to
theorem is added to  to type the
to type the 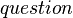 variable.
variable. - The
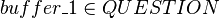 theorem is added to
theorem is added to  to type the
to type the 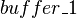 variable.
variable. - The
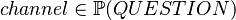 theorem is added to
theorem is added to  to type the
to type the 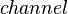 variable.
variable. - The
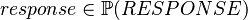 theorem is added to
theorem is added to  to type the
to type the 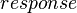 variable.
variable. - The
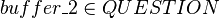 theorem is added to
theorem is added to  to type the
to type the 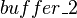 variable.
variable.
The external events
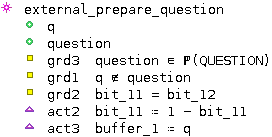
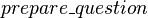 is an event of
is an event of  modifying the
modifying the 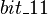 and
and 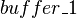 shared variables.
shared variables.
These variables are accessed by the 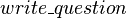 event of
event of  .
.
An external event is therefore built from 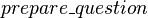 in
in  .
.
Since  does not contain the
does not contain the 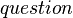 variable, a
variable, a 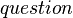 parameter is created.
parameter is created.
Moreover, a guard is added to type it. The QuestionResponse.bcm is parsed to retrieve this typing information.
The 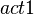 action related to the
action related to the 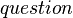 variable is discarded.
variable is discarded.
The 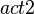 and
and 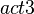 actions are kept.
actions are kept.
In parallel, 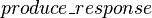 is an event of
is an event of  modifying the
modifying the 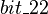 shared variable. This variable is accessed by the
shared variable. This variable is accessed by the 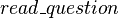 event of
event of  . As a consequence, an external event is built from
. As a consequence, an external event is built from 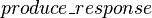 in
in  .
.
In the same manner, 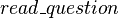 is an event of
is an event of  modifying the
modifying the 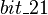 and
and 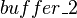 shared variables. These variables are accessed by the
shared variables. These variables are accessed by the 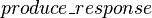 event of
event of  . As a consequence, an external event is built from
. As a consequence, an external event is built from 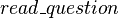 in
in  .
.
Finally, 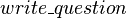 is an event of
is an event of  modifying the
modifying the 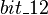 shared variable. This variable is accessed by the
shared variable. This variable is accessed by the 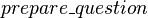 event of
event of  . As a consequence, an external event is built from
. As a consequence, an external event is built from 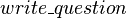 in
in  .
.
The initialization events
The initialization events of the sub-machines are built from the initialization event of  , which is detailed below:
, which is detailed below:

The initialization event of  initializes the variables contained in this sub-machine: the assignments related to the
initializes the variables contained in this sub-machine: the assignments related to the 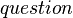 ,
, 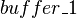 ,
, 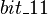 and
and 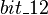 variables are kept; the other assignments are discarded.
variables are kept; the other assignments are discarded.
In the same manner, the initialization event of  initializes the variables contained in this sub-machine: the assignments related to the
initializes the variables contained in this sub-machine: the assignments related to the 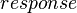 ,
, 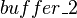 ,
, 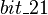 and
and 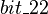 are kept; the other assignments are discarded.
are kept; the other assignments are discarded.
Finally, when building the initialization event of  , the assignments are all kept, except those corresponding to
, the assignments are all kept, except those corresponding to 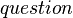 and
and 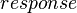 .
.
The contexts
The contexts of the sub-machines are built from the context 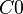 associated to
associated to  :
:
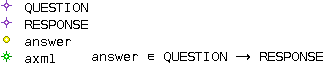
For each sub-machine  , an empty context is created and a SEES clause identifying this context is added in
, an empty context is created and a SEES clause identifying this context is added in  . Then, these contexts are filled:
. Then, these contexts are filled:
 ,
,  and
and  reference the
reference the 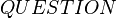 set. It is therefore copied in each context.
set. It is therefore copied in each context.- The
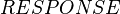 set is only referenced by
set is only referenced by  . It is copied in the associated context.
. It is copied in the associated context. - The
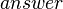 constant is only referenced by
constant is only referenced by  . It is copied in the associated context.
. It is copied in the associated context. - The sets and constants referenced by the
 axiom have been previously copied in the context associated to
axiom have been previously copied in the context associated to  . As a consequence, it is copied in this context too.
. As a consequence, it is copied in this context too.
To summarize, the context seen by  and
and  only contains the
only contains the 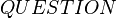 set. The context seen by
set. The context seen by  is equal to
is equal to 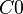 .
.
Implementation
A first plugin prototype is accessible under _exploratory/tshoang/ch.ethz.eventb.decomposition.
Bibliography
- J.R. Abrial, The B-book: assigning programs to meanings, Cambridge University Press, 1996 (ISBN 0-521-49619-5).
- J.R. Abrial, Mathematical Models for Refinement and Decomposition, in Modeling in Event-B: System and Software Engineering, to be published in 2009.
- J.R. Abrial, Event Model Decomposition, Version 1.3, April 2009.
- M. Butler, Decomposition Structures for Event-B, in Integrated Formal Methods iFM2009, Springer, LNCS 5423, 2009.
- M. Butler, Incremental Design of Distributed Systems with Event-B, in Marktoberdorf Summer School 2008 Lecture Notes, 2008.
- M. Poppleton,The composition of Event-B models, in ABZ2008: Int. Conference on ASM, B and Z, 2008.